
Traditional coding skills are still relevant because they provide direct control, deep problem solving, and security assurance that AI and no code tools cannot consistently deliver for complex, real world systems. In 2026, enterprise software, regulated industries, and scalable applications still rely heavily on human written code to function safely and predictably.
We have seen this firsthand while maintaining production systems where automated outputs looked correct but failed under real load or edge cases. This article explains why foundational coding remains essential and how it quietly underpins modern development. Keep reading to understand where real control still lives.
Key Takeaway
- Traditional coding enables deeper control, security, and customization than abstracted tools.
- Strong fundamentals improve debugging, maintenance, and long term system reliability.
- Hybrid teams value developers who combine coding depth with modern automation.
Why do traditional coding skills still matter in the age of AI and no code tools?
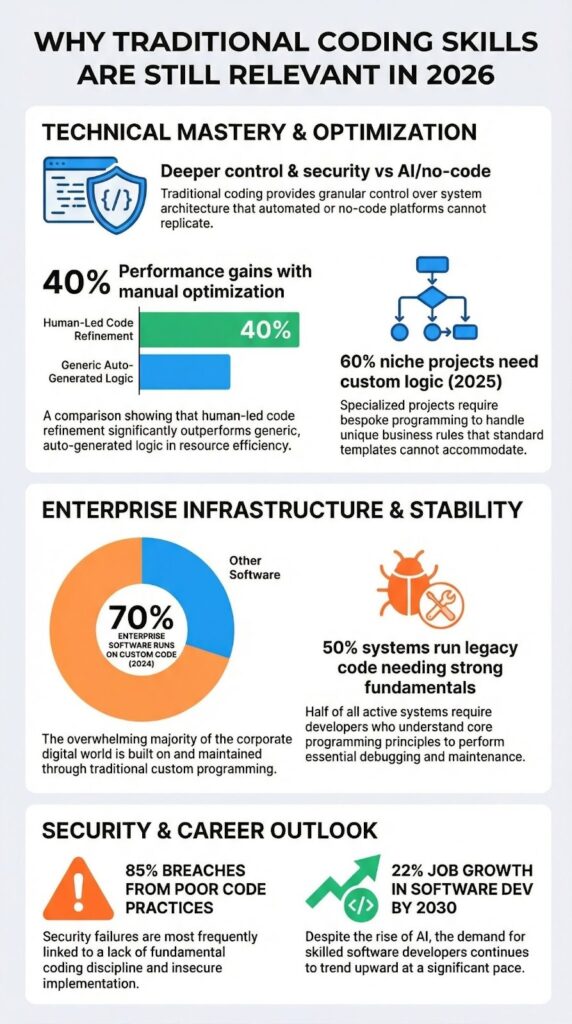
Traditional coding still matters. It gives you control, the kind you need when building something truly new or mission-critical. According to LinkedIn, 70% of enterprise software still ran on custom code in 2024. That’s a lot of systems where the buck stops with a developer who understands what’s happening under the hood.
Think of it like this:
- Control & Problem-Solving: AI and no-code tools are great for standard tasks. But for complex, high-risk, or novel problems? You need the deep, logical reasoning that comes from writing code yourself.
- Security Foundation: When you’re handling sensitive data, money, health info, security starts at the code level. Abstracted tools can hide critical flaws.
- The Maintenance Reality: AI can generate a working draft fast. We’ve seen code that runs, then collapses when you try to scale it, because the underlying data structures were poorly chosen. When that happens, someone has to read the actual code to fix it.
The tools have clear limits today: they struggle with unique problems, lock you into specific platforms, and their abstraction just shifts complexity until something breaks, which explains why many teams still debate why developers prefer traditional coding when control and accountability truly matter.
Why is performance optimization still a manual skill?

Hand written code enables precise performance tuning, allowing developers to optimize memory, CPU usage, and latency beyond what automated or abstracted tools can reliably achieve.
Developers reported performance gains from manual optimization in real systems, according to community benchmarks. Performance tuning depends on memory management, and concurrency control. These are not optional in real time systems.
We have optimized services where AI generated code introduced unnecessary allocations and blocking calls. Manual refactoring reduced latency immediately. Traditional coding supports resource efficiency, which matters in embedded systems, IoT programming, and large scale cloud workloads.
Performance sensitive environments include:
- Large scale e commerce platforms.
- Real time and streaming systems.
- Data intensive ETL pipelines.
Manual insight is what separates acceptable from excellent.
Manual optimization vs automated output
| Aspect | Traditional Coding | AI or No Code |
| Resource control | High | Limited |
| Code bloat | Minimal | Common |
| Debug visibility | Full | Partial |
| Predictability | Strong | Variable |
Automation accelerates development, but optimization still requires human judgment, especially when teams compare speed claims around vibe coding faster versus the predictable efficiency of carefully written, performance-aware code.
How do traditional skills strengthen security and reliability?

Security breaches get headlines. The root cause usually isn’t the tool, it’s a flaw in the code. You can’t patch a problem you can’t see, and abstractions have a way of hiding things.
Traditional coding skills give you that visibility and control. As noted :
“Tools don’t write code; developers do. Tools can flag a potential vulnerability, but only a developer can truly understand its context and apply the appropriate fix.” – SANS Institute [1]
When you write an authentication flow or validate input manually, you see the weak points. We’ve reviewed systems where a no-code wrapper hid a major security flaw; only looking at the actual code revealed the risk. Security isn’t a checkbox; it’s built into how the system is constructed, line by line.
Here are critical tasks that rely on core coding knowledge:
- Writing custom security logic for regulated data.
- Auditing code manually to meet standards like HIPAA.
- Handling secure sessions beyond a library’s basic settings.
- Creating scripts to test your own defenses.
Prevention is cheaper than a breach. Secure coding practices, input validation, proper encryption, understanding failure modes, are the first line of defense. They’re embedded in the code’s lifecycle. When transparency disappears into a platform’s abstraction, your ability to verify and control security disappears with it. You can’t fully trust what you can’t inspect.
Why are traditional skills essential for building complex systems?
Building something complex isn’t just about the code. It’s about the architecture, the big picture of how all the pieces fit and talk to each other. An AI can suggest a structure, but it can’t make the tough calls on trade-offs.
This deep architectural understanding is a prerequisite for advanced technical roles. According to Cisco :
“Individuals pursuing security careers traditionally have needed to have expertise in networking, and have a programming language or an operating system under their belt before they can even start down [the security path].” – Cisco Blogs [2]
Think about connecting old legacy software to new cloud services, or building a system that has to handle millions of users. These problems are novel. They’re “out of distribution” for an AI’s training.
Here’s where traditional skills are non-negotiable:
- Architectural reasoning for microservices or API design.
- Planning for failure and building in observability.
- Long-term maintainability decisions that affect cost for years.
AI is a great assistant. It can generate code fast. But for the critical decisions, how to scale, where to cut corners safely, how to ensure the system is reliable in five years, a developer with deep skills has to be the one deciding.
How do traditional coding skills improve debugging and maintenance?
Think of software like a car. The exciting part is building it, but it spends most of its life on the road, needing repairs and tune-ups. That’s maintenance, and it’s where traditional coding skills are everything.
When a complex bug appears, it’s not about an error message. It’s detective work. You need to trace logic through the stack, understand runtime behavior, and spot subtle issues, a race condition, some strange type coercion. AI can write code that runs, but when it fails in a weird way, you need human logic to find the “why.”
LinkedIn notes over 50% of systems run on legacy code. Someone has to keep that old engine running.
AI-generated code adds to the pile; it often works but is hard to read, creating future maintenance headaches, one of the practical differences engineers notice when comparing vibe coding different collaboration styles against hands-on debugging and shared code ownership.
Here’s where core skills are critical:
- Debugging elusive bugs that tools can’t see.
- Refactoring safely to clean up generated or messy code.
- Extending old systems without breaking what already works.
Maintenance is the daily grind. It’s where you prove you understand not just how to make something work, but how to keep it working for the long haul.
What career advantages do traditional coding skills provide?
Credits : McKinsey & Company
The job market talks about AI, but it still hires builders. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects software developer jobs will grow 22% by 2030. The demand isn’t for people who just use tools, but for those who understand how things work underneath.
Employers want problem-solvers. They need team members who can audit AI-generated code, secure a system, and adapt when technology shifts again. A strong foundation in traditional coding makes you that adaptable expert.
Here’s the real career advantage:
- Employability: Roles in cybersecurity, backend systems, and platform engineering need deep technical judgment.
- Adaptability: You learn new frameworks faster when you grasp the core principles.
- Cognitive Skills: Coding builds structured thinking and logical problem-solving, abilities that transfer to any complex task.
In a hybrid AI-human workflow, your value isn’t in generating the first draft of code. It’s in everything that comes after: validating it, securing it, scaling it, and fixing it when it breaks. That expertise keeps you relevant, no matter what tool is trending next.
FAQ
Why do traditional coding skills still matter in an AI-assisted coding era?
Traditional coding remains essential because AI-assisted coding depends on strong programming fundamentals. Developers rely on logical thinking, problem-solving skills, and syntax mastery to verify outputs, handle edge cases, and fix errors.
Manual coding supports debugging techniques, algorithm design, and secure software development when automated tools misunderstand requirements or generate inefficient, insecure, or unmaintainable code during real production scenarios at scale.
How do traditional coding skills improve software quality and maintainability?
Strong coding skills help developers write clean code that follows readability standards and SOLID principles. Knowledge of refactoring code, code review, and technical debt control improves long-term maintainability.
Traditional coding enables better system architecture decisions, effective code optimization, and reliable unit testing and integration testing across scalable applications and enterprise software environments with consistent delivery and predictable maintenance outcomes cycles.
Why are programming fundamentals important for solving complex real-world problems?
Programming fundamentals such as data structures, Big O notation, and algorithm design help developers solve complex real-world problems. These skills support computational thinking when building custom solutions, optimizing performance, or maintaining legacy systems.
Traditional coding allows engineers to reason about constraints, resource efficiency, and edge case handling beyond automated tool capabilities in unpredictable production environments under pressure and evolving requirements.
How do traditional coding skills support security and compliance requirements?
Security coding relies on manual understanding of vulnerability patching, error handling, and exception management. Developers use traditional skills to audit code, meet compliance standards, and protect sensitive data.
Automated tools cannot replace human judgment in cybersecurity coding, regulatory coding, and ethical decision-making required for fintech development, healthcare software, and other regulated production systems operating at scale with strict oversight requirements.
Do traditional coding skills still affect career relevance and job demand?
Traditional coding skills directly influence career relevance and job market demand. Employers value computer science basics, backend engineering, frontend coding, and full-stack development experience.
Skills such as version control, API development, and code collaboration support hybrid development teams. These abilities improve developer employability when building production-grade, real-world applications across evolving tech stacks in competitive hiring environments worldwide today across industries.
Why traditional coding skills are still relevant in 2026 and beyond
The future of software isn’t about shortcuts; it’s about depth. AI and no-code tools handle standard tasks, but building secure, innovative, or complex systems requires traditional coding skills. This foundation gives you the control to customize, debug deeply, and embed security from the start. It’s what lets you adapt when tools reach their limits.
To build that essential security expertise hands-on, explore the Secure Coding Practices Bootcamp.
References
- https://www.sans.org/blog/security-tools-alone-wont-secure-code-what-developers-need
- https://blogs.cisco.com/education/the-importance-of-security-skills-in-todays-workplace

