
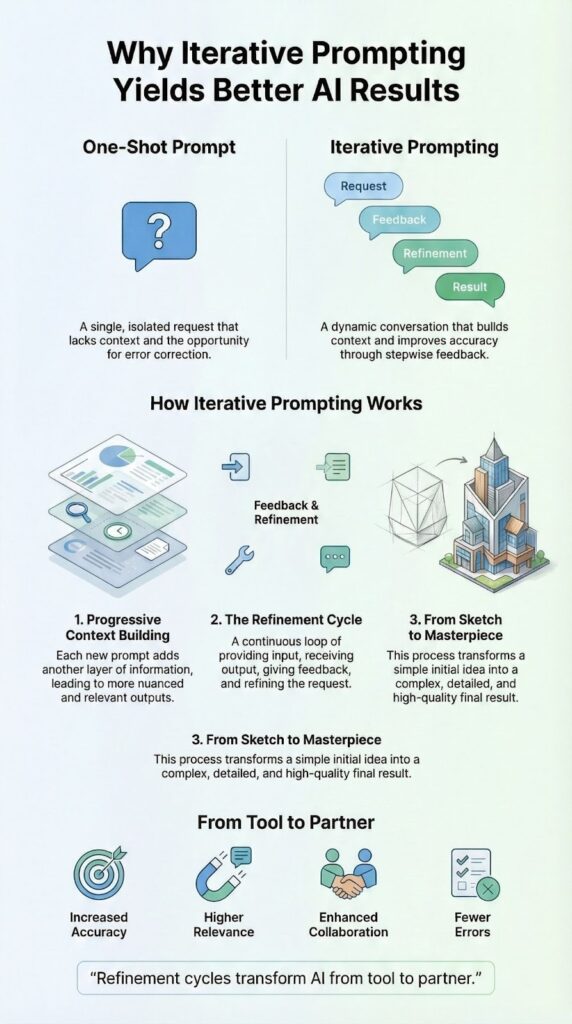
Iterative prompting works better because it matches how people actually think. We rarely nail a problem on the first attempt. We test an idea, see what lands, then sharpen it. That same rhythm turns AI from a clumsy tool into something you can steer with real control.
The first prompt is just the opening line, the follow-ups do the heavy lifting. They fix misreads, add edge cases, and layer in context until the answer feels tailored instead of generic. If you want your AI responses closer to a finished draft than a rough outline, keep reading.
Key Takeaways
- Iterative prompting builds context progressively, leading to more accurate and relevant outputs.
- The method allows for real-time error correction, reducing hallucinations and factual errors.
- This approach transforms AI from a one-time query tool into a collaborative problem-solving partner.
The Fundamental Flaw of One-Shot Prompts
I remember asking an AI to draft a section on secure coding. The answer was correct, but it felt flat, like it came from a training manual. It listed principles, sure, but no real stories, no code-level details that developers actually look for. We wanted it to sound like a senior engineer, not a policy document.
So we pushed it further with follow-up prompts.
- First: “Rewrite this as common mistakes juniors make, plus the secure fix.”
- Then: “For input validation, give me one vulnerable and one secure Python snippet.”
Each turn made the output sharper, more grounded.
That’s the real weakness of one-shot prompts:
- No error correction , the first draft is all you get.
- No gradual focus , you can’t steer based on what you see.
- No real memory , each request stands alone.
Iterative prompting, instead, stacks context. The model sees your goal, its past answers, your feedback, and adjusts. That running history is what turns rough output into something you’d actually use. Keep reading to see how to build that kind of conversation on purpose [1].
How the Iterative Feedback Loop Transforms Output

The real strength of iterative prompting isn’t mystery, it’s a simple feedback loop. You’re not just a user anymore, you’re the editor, shaping a capable but very literal writer.
Here’s how it works in practice:
- Start with a clear, specific goal for the output.
- Write an initial iterative techniques prompt that’s “good enough,” not perfect.
- Use the first answer as a draft, not the final product.
Then you switch into editing mode. You read the response and ask: What works? What feels off? Is the tone right for the reader you have in mind? Are key details missing?
Your next prompt should give focused, concrete feedback, like:
“Remove the jargon in the second paragraph and replace it with an example a beginner would understand.”
You repeat this loop. Each round targets one or two changes: maybe clarity first, then examples, then tone. That narrow focus keeps the model from drifting and pulls the output closer to what you actually wanted at the start. Keep reading to see what this looks like with real prompt examples.
Witnessing the Shift From Generic to Specific
Credits : Learning To Code With AI
You really feel the power of iterative prompting when you watch a vague answer turn into something sharp and useful. Take a simple task: explaining a technical concept.
- Initial prompt: “Explain the concept of SQL injection.”
- The AI gives a standard definition. It’s correct, but you could find the same thing in a basic help article.
- First refinement: “Rewrite that for a web developer new to security. Use a house-building analogy.”
- Now the answer feels more grounded. SQL injection becomes a bad instruction slipped into the plans, and the database is the builder that follows it blindly.
- Second refinement: “Add a basic vulnerable PHP snippet and a fixed version using parameterized queries.”
- Suddenly you get real code. One unsafe query with string concatenation, one safe version with prepared statements.
That jump, from generic definition to practical, developer-ready explanation, comes from stacking prompts with clear intent. Keep reading to see how to design these chains on purpose, not by luck [2].
Practical Strategies for Your Own Workflow

Making iterative prompting part of your work is less about tricks and more about how you see your role. You’re not just asking questions, you’re directing a draft.
Start simple: know your goal before you type. Your first prompts should describe what you want in plain language, audience, tone, length, format. This sets you up for quicker refinement and stronger replies. It doesn’t need to be clever, just clear enough to get a usable first draft.
Then you refine with purpose. Look at the reply and ask:
- Is anything inaccurate or shallow?
- Is the structure messy or hard to follow?
- Is the tone wrong for the reader?
- Are there missing examples or edge cases?
Turn each of those into a focused follow-up prompt, one or two aims per round:
“Restructure this into 3 sections with headings.”
“Keep the content, but rewrite for a beginner.”
“Add two concrete examples and remove vague phrases.”
You can also:
- Ask for pros and cons after an explanation.
- Request alternative takes: “Now argue the opposite.”
- Set a clear success target: “Use under 400 words, and make it skimmable.”
And then, you stop when it’s good enough for the job, not flawless, just ready to use.
The Human Element in AI Conversations
Iterative prompting feels natural because it matches how people actually learn. We don’t absorb complex ideas in one giant download. We ask, listen, question, and narrow in.
When you force everything into one prompt, you’re trying to pack all nuance, all edge cases, into a single shot. That’s hard even between humans. Most real conversations work in layers, and maintaining clarity at each step is key:
- First answer: broad summary.
- Next question: “What about this case?”
- Follow-up: “Explain that in simpler terms.”
AI works best in that same rhythm. Each turn adds context, shared assumptions, and clearer goals. You stop restarting from zero and start building on a shared base.
This doesn’t actually slow you down. Three quick, focused prompts that land on a strong answer usually beat one “perfect” prompt that still needs heavy editing.
The most effective prompts often sound like normal speech:
- “That’s a good start, make the tone more casual, like you’re talking to a coworker.”
- “Keep the house analogy, now give me a second one using a restaurant.”
With this mindset, a weak reply isn’t a dead end, it’s just the next draft on the way to something useful.
FAQ
What is iterative prompting, and how does it improve AI output quality?
Iterative prompting is a method where prompts are refined through multiple cycles to improve results. By using successive refinement, incremental prompting, and feedback-driven prompting, each iteration aligns AI responses more closely with user goals. This process reduces errors, accumulates context effectively, and ensures outputs are precise, relevant, and consistently higher in quality over time.
How does multi-turn interaction benefit from prompt refinement techniques?
Multi-turn interaction improves AI outputs by applying conversational prompting and stepwise prompting across a sequence of exchanges. Each step allows the AI to integrate previous context, correct misunderstandings, and refine its responses. Techniques like adaptive prompting and layered refinement make interactions more accurate and coherent, producing outputs that better match user intent over multiple conversational turns.
Why is feedback loop prompting important in iterative AI workflows?
Feedback loop prompting is essential for iterative refinement and prompt optimization loops. By reviewing outputs and providing corrections, users guide the AI toward more accurate results. Techniques such as error correction prompting, precision iteration, and prompt tuning processes help eliminate mistakes, ensuring responses remain consistent, relevant, and closely aligned with the intended objectives.
Can sequential prompting reduce mistakes in AI-generated responses?
Yes, sequential prompting and stepwise refinement reduce errors by building context gradually. Each prompt iteration incorporates previous insights, using prompt chaining, successive approximation, and multi-step prompting. Structuring prompts in layers allows the AI to produce logically coherent and precise responses, creating a reliable, error-minimizing workflow that aligns closely with user expectations.
How does adaptive prompting support evolving user goals in AI tasks?
Adaptive prompting adjusts outputs dynamically using iterative feedback, contextual iteration, and progressive prompt engineering. As user objectives evolve, prompts change to guide the AI toward more relevant results. This approach ensures continuous response refinement and prompt evolution cycles, producing outputs that remain accurate, context-aware, and tailored to shifting goals without requiring repetitive manual corrections.
The Final Refinement
Iterative prompting works because it accepts a simple truth: real quality comes from revision, not from a lucky first try. Instead of treating AI like an oracle that spits out final answers, you treat it like a thinking partner you can shape through back-and-forth. The first prompt is just your opening move. Each refinement adds context, tests a direction, and sharpens the output until it actually matches what you had in mind.
If you want to apply that same mindset to your code, and learn to spot and fix security flaws through real, hands-on practice, check out the Secure Coding Bootcamp.
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prompt_injection
- https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/iterative-prompting

