
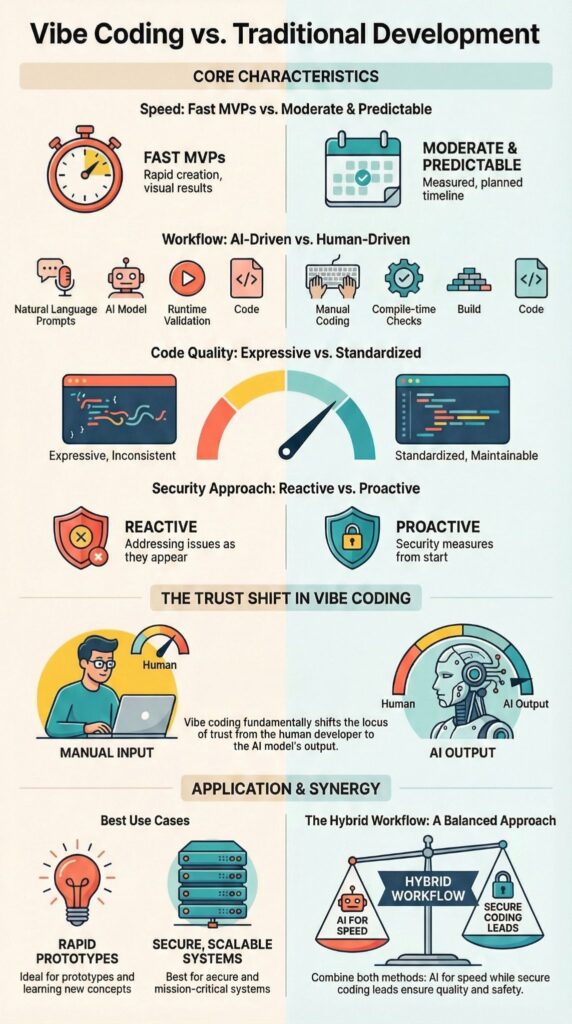
Vibe coding and traditional development solve the same problem in very different ways. Vibe coding uses natural language prompts and AI driven development to generate working software fast. Traditional development relies on manual code writing, structured planning, and deep technical review.
Both approaches work, and both fail, depending on context. We have used each in real projects, felt the rush of prototype acceleration, and paid the price of long term maintenance costs. The difference is not ideology. It is risk tolerance. Keep reading if you want clarity instead of hype.
Key Takeaway
- Vibe coding boosts startup velocity but shifts trust from humans to models
- Traditional development protects reliability, security, and scale
- Hybrid workflows work best when Secure Coding Practices lead the process
How Is Vibe Coding Different From Pair Programming
Sometimes what throws people off is how similar vibe coding looks to two developers huddled at one keyboard, talking their way through a problem. On the surface, it feels like pair programming. Underneath, it’s not.
In classic pair programming, both humans share mental ownership of the code. They might disagree, debate, or refactor, but they both know why a line exists. In vibe coding, our learners often watch the AI generate logic they never fully read, let alone understand. The code “works,” but the intent lives mostly in the model’s hidden reasoning, not in the team’s heads.
We see the sharpest contrast when something breaks.
- In pair programming, the path to a fix is traceable. You remember the discussion, you can replay the decisions, and you can step through the code together.
- In vibe coding, the reasoning chain is mostly opaque. The model patches its own output, new code layers over old, and error propagation risks rise because no one fully owns the mental model.
So while vibe coding feels collaborative, there’s a back‑and‑forth, there’s dialogue, it behaves far more autonomously [1].
Is Vibe Coding Faster Than Writing Code Manually

For rapid prototyping and exploratory work, vibe coding really does feel faster, especially when teams lean on vibe coding patterns that favor speed of execution over early structural guarantees.
We’ve watched students walk into our secure dev bootcamp with only an idea and leave a few hours later with a working demo. The AI fills in boilerplate, stitches together APIs, and lets them “talk” features into existence before a traditional sprint would even finish grooming tickets.
Manual coding starts to pull ahead when the bar moves from “it runs” to “it runs well, safely, and at scale.” Performance tuning, modular architecture, threat modeling, and compliance checks are still very human‑driven in our experience. Teams that rely only on vibe coding usually hit a wall once they need guarantees, not just output.
Speed also shifts with the phase of the project:
- Early ideation tends to favor a high AI‑generated code percentage.
- Refinement and hardening lean toward traditional rigor and code review.
- Long‑term maintenance rewards structured planning, clear ownership, and secure design.
We’ve seen early deployment wins from vibe coding vanish once systems needed refactoring, security audits, or serious debugging. That’s where the “fast” feeling quickly flips, and our secure development playbook has to step in.
Why Some Developers Prefer Traditional Coding
Some of the most grounded conversations we have in our bootcamps happen when someone says, “I just want to know exactly what my code is doing.” That’s where traditional coding still feels like home for a lot of developers.
Traditional development gives them direct control. Every line is intentional, every dependency is picked on purpose, not because a model thought it “looked right.” In our secure development sessions, that control becomes more than a preference, it’s the difference between guessing and knowing when you’re handling secrets, tokens, or payment flows.
That control shows up in familiar workflows:
- Version control (Git) for traceability and code history
- IDE debugging and structured testing frameworks
- Design patterns like SOLID to keep codebases maintainable and reviewable
Cloudflare’s Learning Center points out that secure software depends on understanding how code handles data and failure states. We’ve seen that play out directly with our learners: when they wrote the logic themselves, they could walk us through edge cases; when a model wrote it, they often couldn’t explain what happened on a bad input or partial outage.
When Should You Use a Vibe Coding Workflow
Sometimes the better question isn’t “Can I use vibe coding?” but “What happens if this breaks in the real world?”
Vibe coding works best when the goals are learning, ideation speed, or quick MVPs. In our secure development bootcamps, we’ve watched learners spin up disposable tools and internal experiments in a single session, as long as the problem is clearly described and the blast radius is low, no production data, no external users, no critical paths.
Good use cases usually look like:
- Proofs of concept under tight deadlines
- Boilerplate automation for patterns we already understand well
- Exploratory projects to test user interest or interface ideas
Where we get cautious is anything with long‑term ownership or real risk. If a system needs to be maintained for years, audited, or trusted with sensitive data, a pure vibe workflow tends to crack under pressure. Compliance and serious security concerns don’t mix well with opaque reasoning chains.
For those projects, Secure Coding Practices come first. We start with threat modeling, input validation, and access control design, then decide where AI can safely assist.
Comparing Pros and Cons for Senior Developers
One of the more honest reactions we hear from seniors in our bootcamps is, “I’m faster, but I feel weirdly weaker.” That’s the tradeoff many of them run into with vibe coding.
On paper, senior developers gain a lot. AI tools cut down Stack Overflow searches, generate boilerplate, and clear away repetitive tasks. In our sessions, we’ve seen seniors ship small features faster than ever by offloading glue code to the model. But the leverage they built over years, knowing where to look, how to shape a system, starts to slip when they’re debugging logic they never designed.
The pain points tend to cluster around a few areas:
- Handling LLM hallucinations inside complex, stateful systems
- Letting prompt specificity stand in for real architectural decisions
- Losing visibility into performance and resource bottlenecks hidden in AI‑generated layers
What they gain is ideation speed: more experiments, more “what if” branches, more prototypes in less time. What they give up, if they’re not careful, is intuition about how the system behaves under stress, under attack, or under real‑world traffic. In secure development, that intuition isn’t a luxury for seniors, it’s part of the job.
What Are the Key Workflow Differences
Sometimes you can see the workflow split before any “real” coding starts, right in how people choose to begin.
In traditional development, teams usually lead with structure: planning, architecture, and risk analysis before anyone touches implementation. In our secure development bootcamps, we watch seniors sketch data flows, define trust boundaries, and agree on failure handling. The code grows out of that shared understanding.
Vibe coding reverses that order. Execution leads; understanding catches up later. A developer describes the goal in natural language, the model generates code, and only after running it do they start asking what the system is actually doing. We’ve seen learners get a working feature on screen while still being unsure how data and permissions are handled underneath.
You can think of the core patterns like this:
- Traditional: plan → design → implement → test
- Vibe coding: describe → generate → run → inspect
And side by side:
| Dimension | Vibe Coding | Traditional Development |
| Primary input | Natural language prompts | Manual code writing |
| Validation | Runtime evaluation | Compile-time checks and tests |
| Speed | High for MVPs | Moderate, more predictable |
| Code quality | Expressive, inconsistent | Standardized, maintainable |
| Security posture | Reactive | Proactive |
How Does Code Quality Compare Between Methods
With vibe‑coded systems, we keep seeing the same pattern in our bootcamps. The app runs, the feature demo looks good, but the code underneath feels scattered. Naming is inconsistent, patterns drift between files, and dependencies sprawl in ways no one fully tracks. It works, but it doesn’t feel like a system you’d want to bet on.
Traditional development leans much harder on structure and shared discipline, using:
- Linting and formatting rules
- Code reviews to enforce standards and catch logic issues
- Team conventions and patterns for predictable structure
Wikipedia’s overview of secure coding notes that many vulnerabilities come from subtle logic errors, not syntax problems. We see that constantly. The serious bugs hide in data handling, branching logic, and authorization flows, areas that are easy to miss if nobody sits down to read and reason through the code.
At our secure development bootcamp, Secure Coding Practices are the baseline, not an optional extra. For us, that means reviewing AI output, enforcing validation at boundaries, and applying least‑privilege access, even for prototypes. Without that discipline, vibe‑based trust models tend to fail fast once real users and real threats enter the picture.
Is One Better for Rapid Software Prototyping
For raw speed, vibe coding usually wins. In our secure development bootcamps, we’ve watched learners go from a vague idea to a live demo in a single session using chat‑based feedback and almost no manual editing. You’re testing ideas, reactions, and flows more than you’re testing architecture.
The catch shows up when a “quick prototype” quietly turns into the first version of a real product. That’s where we’ve seen teams get stuck. Early vibe‑driven choices, ad‑hoc data models, leaky access control, tightly coupled services, can harden into brittle structures. More than once, we’ve watched companies decide it’s safer and cheaper to rewrite whole systems than to slowly patch their way out of those early decisions.
From what we’ve seen, a hybrid model works best:
- Use vibe coding to explore: spike features, validate ideas, try multiple variations fast.
- Use traditional methods to solidify: design the architecture, implement security controls, refactor for clarity and ownership.
We keep telling our learners: vibe is great for getting you to “something.” Secure, maintainable software still needs deliberate, old‑fashioned engineering on top.
How It Changes the Core Role of a Programmer

Instead of acting purely as builders, developers are sliding into a mix of editor and curator. With AI copilots and vibe workflows, they spend more time describing problems, constraints, and goals, and a lot less time manually typing every solution. The keyboard work shrinks; the thinking work doesn’t.
That change raises uncomfortable questions about who counts as an “expert.” If almost anyone can write a prompt and get working code, where does seniority live? We hear that worry a lot from experienced engineers who join our secure development training.
In practice, expertise still matters; it just moves upstream. We see it every week:
- Experienced developers write sharper prompts that actually match the real problem.
- They spot flawed logic and missing checks much faster.
- They know when not to trust the model and when to fall back to manual design.
The role of the programmer starts to look less like a typist of instructions and more like a judge of solutions, someone responsible for what ships, not just for what gets generated.
Why Traditional Coding Skills Are Still Relevant
Credits : Top Front Dev
Traditional coding skills anchor everything. When a developer understands algorithms, data structures, and system design, they don’t just consume AI output, they shape it. Their prompts are sharper, their reviews are tougher, and their ability to say, “This looks clever but wrong,” is much higher. Without that foundation, prompt skills hit a ceiling fast.
We see traditional knowledge paying off in areas like:
- Debugging behavior in complex, multi-service systems
- Designing validation that goes far beyond the happy path
- Estimating long‑term maintenance and security costs
From our perspective, the future isn’t vibe versus traditional; it’s integration with clear boundaries. In a secure development setting, those boundaries come from Secure Coding Practices. That’s how we decide:
- Where AI can safely accelerate boilerplate or exploration
- Where we need to slow down, design deliberately, and verify trust assumptions
We lean on AI as a power tool, not a replacement for engineering judgment. The foundation still has to come from real, traditional coding skill [2].
FAQ
How does vibe coding change the development workflow compared to traditional methods?
Vibe coding introduces a development paradigm shift through AI-driven development and conversational coding. Developers rely on natural language prompts instead of manual code writing and detailed upfront planning. This approach enables rapid prototyping, prototype acceleration, and faster ideation. Traditional development follows waterfall phases or agile sprints, using structured planning, version control Git, and defined handoff stages.
Can non-coders realistically build functional applications using vibe coding?
Vibe coding enables non-coder empowerment through syntax-free programming and LLM code generation. Users describe goals in plain language and refine outputs through chat-based feedback and prompt iteration loops. This lowers the technical expertise requirement and improves beginner accessibility. However, clear problem descriptions and basic prompt engineering skills remain necessary for reliable results.
What are the main code quality differences between vibe coding and traditional development?
Vibe coding accelerates MVP building and exploratory projects but often sacrifices consistency and structure. Common issues include expressive inconsistencies, missing static analysis, and the absence of compile-time checks. Traditional development prioritizes modular architecture, SOLID design patterns, code linting, and maintainable codebases. These practices support enterprise scalability, performance optimization, and long-term reliability.
How does vibe coding approach debugging, testing, and validation?
Vibe coding relies on iterative testing, runtime evaluation, and execution-based validation rather than IDE debugging and formal testing frameworks. This no-edit coding model speeds experimentation but increases debugging challenges and error propagation risks. Handling LLM hallucinations requires careful validation strategies. Complex systems usually benefit from hybrid development models that combine AI output with human review.
Is vibe coding suitable for security-critical or large-scale production systems?
Vibe coding delivers deployment speed gains and startup velocity boosts, but it introduces serious risks for security-critical code. Issues include data exposure risks, code review bypass, and weak security risk mitigation. Traditional rigor provides controlled reviews, clear code ownership, and predictable production reliability. Many teams adopt hybrid development models to balance innovation speed with long-term stability and cost control.
Vibe Coding vs. Traditional Development in Practice
Vibe coding vs. traditional development is not a moral choice. It is an economic and risk‑based one. Innovation speed tradeoffs are real. So are security failures. The smartest teams mix approaches deliberately. They respect the benefits of traditional rigor while using AI to gain momentum where it’s safe to do so.
The workflow revolution is here. The responsibility, for security, for reliability, for long‑term ownership, remains ours. Level up your team’s secure development skills with the Secure Coding Practices Bootcamp , a 2‑day, hands-on program focused on real-world code, OWASP Top 10, and practical defenses you can apply immediately.
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vibe_coding
- https://www.hostinger.com/tutorials/vibe-coding-vs-traditional-coding

