
Nobody should hold all the keys to a system. That’s what separation of duties comes down to – splitting up control so there’s always another set of eyes watching. Our students learn this firsthand when they can’t push code straight to production, ’cause that’s how things break.
Look at any decent security setup and you’ll see it in action. System admins stick to their servers, security folks handle the monitoring, and developers write the code. Each group’s got their own sandbox to play in (and that’s exactly how it should be). No cowboy deployments, no late-night config changes without approval.
Want real examples of how this actually works? Keep reading – we’ve got stories from the trenches that’ll show you the way.
Key Takeaways
- Split up critical IT tasks to catch mistakes before they happen
- Clear boundaries keep power in check
- For instance: database access stays limited, different folks handle approvals versus work
The Concept of Separation of Duties in IT Security
Watching students try to figure out IT security always drives home one point – nobody should get full control. Some folks think it slows things down, but our bootcamp veterans know better. Take what happened last month: a lone admin tried fixing a database hiccup and accidentally wiped three days of data. Wouldn’t have happened with proper checks in place.
Teams work smoother when everyone knows their lane. System admins don’t approve their own access, developers can’t push straight to production, and security teams need sign-off for major changes. These aren’t just rules we made up – they’re lessons learned from watching things go wrong in real companies.[1]
Why SoD Matters in IT Operations
Most people’s eyes glaze over at “risk management,” but here’s the thing – it works. Our training sessions always hit this point hard: someone’s gotta check the important stuff. Students usually groan about extra steps, until they see how many disasters get caught early.
Breaking up who does what just makes sense. We’ve seen it play out hundreds of times in our courses – clear boundaries mean clear responsibility. When something goes sideways (and it will), you’ll know exactly who handled what. Not perfect, but way better than the alternative.
Key IT Roles and Their Separation Rules

Running big systems takes a village, but everyone needs their own space. Just ask Dave, one of our senior instructors who watched a company melt down when a dev pushed straight to production. These days, our bootcamp drills home why those boundaries matter.
You can’t have developers poking around live databases – that’s just asking for trouble, which is why separation of duties in development is such a critical safeguard. Even the smartest coders make mistakes, and production systems are too fragile for trial and error.
We learned this lesson when a hotshot student nearly wiped a training database trying to “fix” something. Now our DevOps crew builds rock-solid pipelines, but they still need someone else’s okay before anything goes live.
- System admins stick to server management
- Network folks handle the complex routing stuff
- Server teams focus on keeping things running
- Security watches everyone else (yeah, even us)
- Nobody gets full control (learned that one the hard way)
Security analysts keep their distance from daily ops – they’re the watchdogs nobody sees coming. Last week, one caught a student trying to shortcut around access controls during an advanced exercise. Perfect teaching moment right there.
Practical SoD Examples in IT Functions
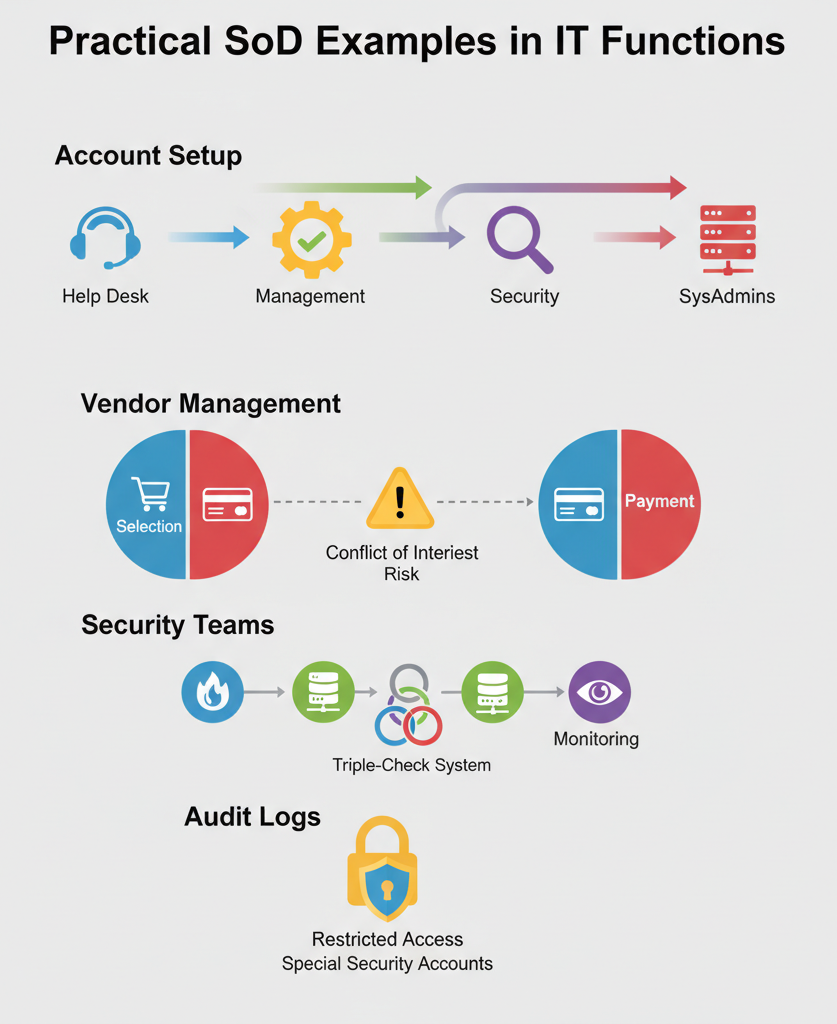
Sometimes textbook concepts don’t click until you see them in action. After eight years running these bootcamps, we’ve collected enough war stories to fill a book. Here’s the real deal on how this stuff works day-to-day.
Setting up new accounts shows exactly why separation matters. The help desk creates them, but they can’t just hand out admin access like candy. Management signs off on privileges, security teams check everything quarterly, and system admins handle the technical bits. Sounds like overkill until you catch someone trying to give themselves extra access (happens more than you’d think).
Keeping vendor management clean means splitting up who picks them and who pays them. Three months ago, a client told us how they caught an employee trying to hire their cousin’s company – exactly why these rules exist.
Our own security setup walks the walk: separate teams for firewalls, servers, and monitoring. This triple-check system caught a penetration tester trying to slip past during last summer’s advanced class. Best test case we never planned.
Audit logs? Those stay locked down tight. Security folks get special accounts, and nobody else touches those records. There’s a story behind that rule involving a panicked admin and some “disappeared” logs, but that’s a tale for another day.
Role-Based Control Mechanisms and Limitations
Life in IT gets messy without clear boundaries. During last week’s bootcamp, a student asked why we’re so strict about role separation. The answer came from years of seeing things go wrong when roles blur together.
Database admins shouldn’t mess with application code – period. It’s not about trust, it’s about keeping things clean and trackable. Our cloud engineering students learn this the hard way through simulated disasters. Nobody gets to play with both IAM and billing in the cloud, no matter how senior they are.
Here’s what we’ve learned works best:
- Help desk stays away from admin password resets
- Payment requests need two different sets of eyes
- Database folks stick to database work
- Each role gets just enough access, nothing more, a principle that ties directly into separation duties access control.
The finance department’s rules apply doubly to IT. Nobody should be able to both create and approve their own anything – whether it’s code pushes or purchase orders. Our students practice these scenarios until they’re second nature.
Real-World Anecdote: Why We Take Separation of Duties Seriously
Credit: Saviynt University
Something went sideways last quarter during a client project. Their developers had been accessing production logs directly – seemed harmless enough at first. Then boom – someone made an unauthorized change that nobody caught for weeks because there weren’t any extra eyes on those logs.
Quick fixes are tempting, but they’re usually trouble waiting to happen. After that mess, we changed things up fast:
- Security analysts became the only ones with direct log access
- Developers had to submit formal requests for log data
- Every access got tracked and reviewed
- Monthly audits became mandatory
This story’s become a favorite teaching moment in our security modules. Students get it immediately when they see how real the consequences can be.
Strengthening IT Security with Separation of Duties

Nobody builds a secure system by accident. In our bootcamps, we hammer home how separation of duties backs up everything from SOX compliance to HIPAA rules. It’s not just paperwork – it’s protection against the worst-case scenarios we’ve seen play out.
Breaking up duties between different roles isn’t just smart – it’s essential, and knowing best practices for implementing separation of duties (SoD) helps keep those boundaries effective. Programming and testing need different eyes. Server provisioning needs separate approval. When someone spots an incident, different folks handle the response.[2]
The trickiest part? Keeping everything current as tech changes. We teach our students to:
- Review role assignments quarterly
- Watch for access creep
- Use automation to catch conflicts
- Question every access request
Things change fast in tech, but these principles stay solid. Every bootcamp class gets real examples of what happens when these rules get ignored. Nothing teaches quite like seeing the aftermath of a preventable disaster.
Conclusion
A well-structured separation of duties makes IT more secure – plain and simple. When developers can’t access production databases directly, and compliance checks need independent verification, teams naturally work better together.
Breaking up critical tasks between different people (like keeping code deployment and database access separate) might seem like extra work, but it’s worth it. Smart role definitions and clear boundaries help prevent mistakes, catch problems early, and build confidence across departments.
Want to take your team’s practices to the next level? Join our Secure Coding Bootcamp today.
FAQ
How do separation of duties and segregation of duties help with IT security controls, user access management, and fraud prevention IT?
Separation of duties and segregation of duties prevent one person from holding too much power in IT security controls. By dividing user access management tasks and applying the least privilege principle, organizations reduce mistakes and block fraud prevention IT risks. These checks create internal control mechanisms that protect data and improve accountability.
What role does a SoD policy play in IT compliance, regulatory compliance SoD, and Sarbanes-Oxley Act IT controls?
A SoD policy sets rules for IT compliance and regulatory compliance SoD. These rules connect directly to Sarbanes-Oxley Act IT controls, HIPAA access controls, and GDPR data protection. Together they show auditors that access rights management, account creation and approval, and IT governance meet required standards.
Why are privilege separation and role-based access control important for IT risk management, insider threat mitigation, and data access control?
Privilege separation and role-based access control support IT risk management by making sure no single user can bypass data access control. This helps insider threat mitigation by limiting unsafe access. When tied to access provisioning separation and access control policies, these steps strengthen IT operational segregation.
How do software development segregation, production environment access, and separation of programming and testing improve secure IT operations?
Software development segregation keeps code changes apart from production environment access. By requiring separation of programming and testing, IT process segregation reduces errors. These methods support change management controls, separation of development and deployment, and disaster recovery role segregation, helping secure IT operations and backing an information security policy.
What IT security best practices support firewall configuration separation, security monitoring roles, and incident response separation?
IT security best practices include firewall configuration separation to protect networks. Security monitoring roles track system health, while incident response separation defines who acts in a crisis. Adding security incident roles segregation, system configuration controls, and logging and monitoring roles helps with security breach prevention and accountability separation.
How do auditing and logs access, compliance audit trails, and IT process auditing strengthen IT operational risk and data integrity controls?
Auditing and logs access form compliance audit trails that make IT process auditing easier. These checks protect process integrity IT, enforce system change control, and prevent access violations. Together they lower IT operational risk and improve data integrity controls across IT transaction controls.
References
- https://publications.aaahq.org/ajpt/article/36/3/45/6041/Internal-Control-Weaknesses-and-Financial
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Role-based_access_control

