Security isn’t some vague idea, it’s set before anyone even touches a device. Most breaches happen because new systems come unlocked, like handing over keys to a fortress with the door wide open. Some clients get stuck with devices that are easy targets right out of the box, while others start off protected.
That’s the power of secure default configurations: they act like a silent guard, working without needing a specialist on call. It’s simple, but it makes all the difference. Keep reading to see how these defaults can change the game.
Key Takeaways
- Out-of-the-box security settings make or break a system’s defense against attacks
- Real-world examples show how proper defaults (like blocked SSH root access) stop hackers cold
- Regular testing and documentation keeps secure defaults working as intended
Secure Default Configurations in IT Systems

Opening a new server or app shouldn’t feel like cutting the wrong wire in a bomb movie. Yet that’s exactly what we face when defaults ship with gaping security holes. Our training sessions always start with this reality check – every system needs solid security from minute one, not as an afterthought.
The best defaults lock things down tight from the start. No unnecessary services running, strict password rules in place, and permissions locked to bare minimums. We’ve cleaned up too many messes from systems that shipped wide open, and it’s always harder to fix things after they’re live.
Why Secure Defaults Matter
Every week our team gets calls about compromised systems, and the story’s usually the same – someone forgot to change those dangerous factory settings. Default credentials are like leaving the keys in your car with the engine running.[1] One missed setting can undo months of careful security work.
Nobody wants to be that admin who left a default password unchanged. But it happens, especially to folks without deep security knowledge. That’s why secure defaults and fail-safe design matter so much, they protect everyone, not just the experts.
Common Threats Exploiting Insecure Defaults
Hackers love hunting for unchanged admin passwords and unnecessary open ports. They’ll try ‘admin/admin’ on every new device they find. Our pen testing reveals the same weak spots: unencrypted data transfers, missing security headers, and overly generous permissions. Basic stuff that secure defaults would’ve prevented entirely.
Examples of Secure Default Configurations Across Platforms and Services
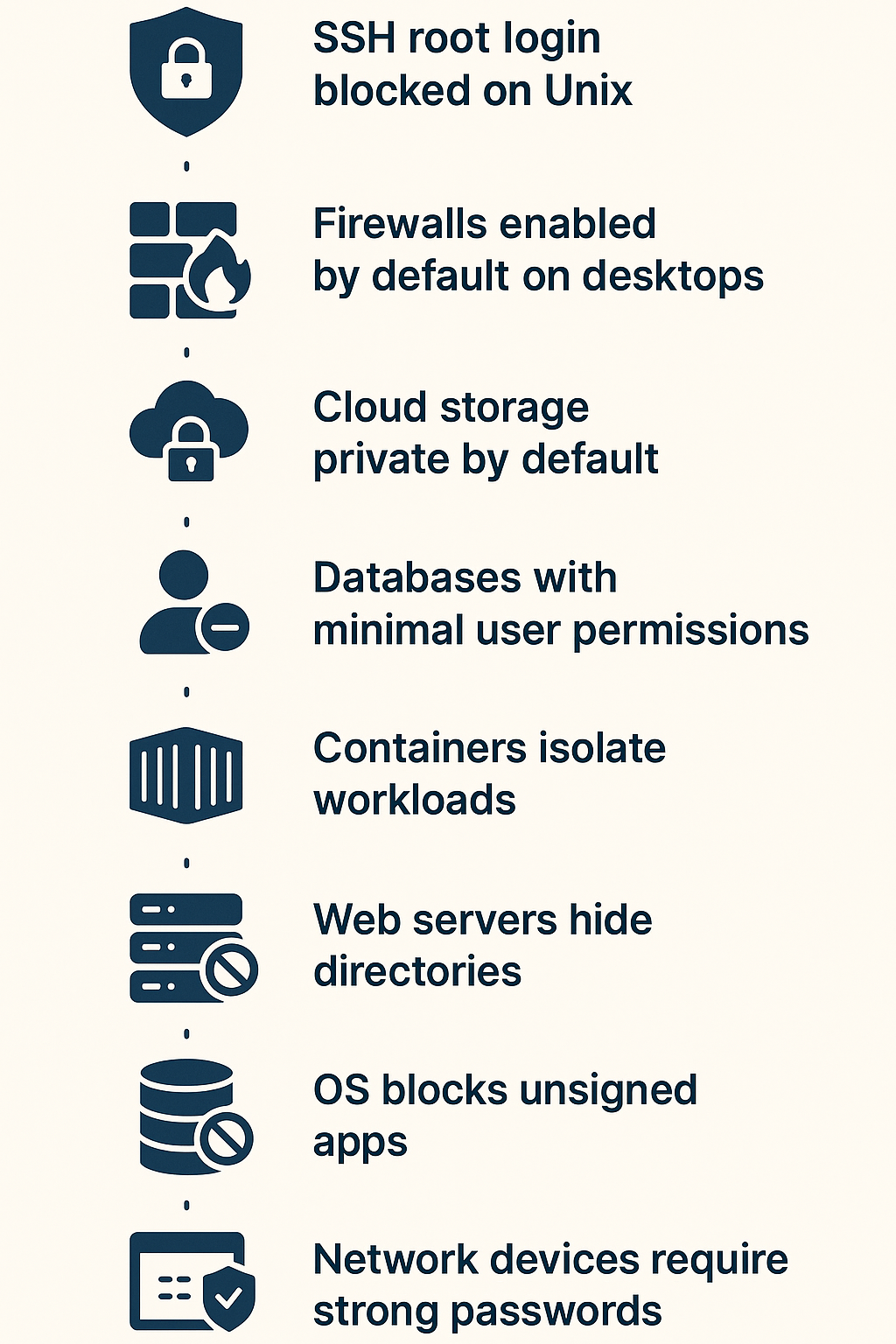
Spend enough time in security, and you’ll see how proper defaults make or break a system’s defense. Here’s what works in the real world:
- Many Unix-based systems block SSH root login automatically, it’s saved our students countless times from brute force attacks. Nobody gets to guess root passwords remotely.
- Modern desktop operating systems ship with their firewalls up and running. Makes a huge difference when machines hit public networks for the first time.
- Cloud storage services now often start private by default. Just last month, our team caught a near-miss where a storage bucket almost went public. Thank goodness for locked-down defaults that made us double-check before exposing data.
- Most modern databases create new users with bare minimum permissions. We’ve seen too many disasters caused by overprivileged accounts.
- Container platforms isolate workloads by default, keeping apps in their own lanes. It’s prevented more than a few “oops” moments in our dev environments.
Sometimes the simplest defaults work best:
- Web servers hiding directory contents
- Databases rejecting remote connections unless allowed
- Operating systems blocking unsigned apps
- Network devices demanding strong passwords
Each one stopped attacks before they started. Sure, you might need to change these defaults sometimes, but they’ve saved our students from the most common security pitfalls.
Security Benefits and Risk Mitigation from Secure Default Configurations
Credit: Threatscape
After running countless security assessments, one truth always stands out, the importance of secure defaults matters more than fancy security tools. When a system ships locked down tight, it stops problems before they start.
Think about what happens in the real world:
- Admins get busy and forget to change settings
- New developers inherit systems they don’t fully understand
- Security patches get delayed or missed entirely
We’ve watched clients dodge bullets just because their systems came pre-hardened. Last month, a student’s test server survived a massive breach attempt – all thanks to disabled root login and proper firewall defaults.[2]
The best part? Good defaults do the heavy lifting without anyone noticing.
They’re like having a security guard who:
- Blocks unnecessary services automatically
- Enforces encryption on sensitive data
- Keeps permissions tight and limited
- Stops common attack patterns cold
Sure, we still need regular security updates and monitoring. But starting from a locked-down position means fewer sleepless nights wondering if someone forgot to close a critical security hole.
Our training always emphasizes this – secure defaults aren’t just convenient, they’re essential survival tools in today’s threat landscape.
Best Practices for Implementing and Maintaining Secure Default Configurations

Setting up solid defaults is just the beginning, implementing fail-safe defaults means keeping them strong through testing, audits, and automation. Through years of training developers, we’ve seen how quickly things can unravel without proper maintenance.
First things first, test everything. Nothing’s worse than locking down a system so tight that normal users can’t do their jobs. Our students learn this the hard way when they accidentally block legitimate traffic with overzealous firewalls.
Key practices that save headaches:
• Write down what each setting does and why it matters
• Use automation to keep configurations consistent
• Check regularly for settings that drift from baseline
• Lock down those config files with encryption
Regular audits catch problems early. Just last week, a client’s security scan revealed default credentials still active on three backup servers. Nobody remembered they existed until the scan flagged them.
The tricky part? Balancing security with usability. Too strict, and users find workarounds. Too loose, and you might as well leave the door open. please rewrite this section aiming to 5th grade readability, keep the writing styles, tone and pov
Remember – defaults aren’t set-and-forget. They need constant attention, just like any other security control.
Conclusion
Setting up systems with secure defaults is a practical way we protect infrastructure and data. It’s not magic but common sense: start locked down, then open what’s needed, not the other way around.
No matter if we’re running servers, cloud tools, containers, or network gear, starting with safe default settings is the first step we lean on. It cuts down the risk and helps keep attackers out. Taking the time to understand and maintain these defaults pays off in resilience and peace of mind.
Ready to build on that foundation? Join our secure bootcamp now
FAQ
What is a secure default configuration, and how do secure config best practices help with secure system configuration?
A secure default configuration means systems start out locked down with safe default security settings instead of being open. Secure config best practices guide how to set secure by default rules for operating systems, applications, and devices. This includes secure server configuration, secure software configuration, and secure router configuration so attackers can’t slip in through weak points.
Why is disabling unnecessary services and managing default password security important for default access control?
Disabled unnecessary services close backdoors that hackers love to use. Along with default password security and default account security, these steps lower risk and strengthen default access control. Secure default passwords and default user permissions also stop attackers from taking easy paths into a network.
How do default network security and firewall default rules reduce risks alongside secure headers defaults?
Default network security and firewall default rules act like locked gates for systems. Secure headers defaults and secure application defaults add another layer by stopping unsafe traffic at the software level. Together, these default security policies and secure authorization settings form a stronger security baseline.
What role does the least privilege principle play in secure operating system defaults and multi-factor authentication defaults?
The least privilege principle means users only get the access they need, nothing more. This ties into secure operating system defaults and default user permissions. With multi-factor authentication defaults and default service hardening, attackers face extra hurdles, lowering chances of a full system breach.
How does secure server configuration support security baseline configurations and configuration management security?
A secure server configuration is a pillar of strong systems. Security baseline configurations and configuration management security keep default security compliance in check. Secure config auditing, automated secure config, and secure defaults testing help catch drift and make sure systems stick to the secure configuration baseline.
Why do secure network protocols and secure service settings matter for default encryption settings and secure cloud defaults?
Secure network protocols and secure service settings keep data safe in motion. They work with default encryption settings, default secure communication, and default data encryption. Secure cloud defaults and secure database defaults also rely on these layers, making default secure storage and default security logs much safer.
How does initial secure setup and default system hardening help enforce minimal attack surface defaults?
Initial secure setup with default system hardening strips systems down to what’s needed. Minimal attack surface defaults mean fewer cracks for attackers. This includes default patch management, default security scanning, and default ransomware protection. Adding secure device defaults and secure default firewall rules makes defenses even tighter.
How do default secure TLS settings and secure software deployment connect with configuration vulnerability management?
Default secure TLS settings keep web traffic locked down. When paired with secure software deployment and default secure coding practices, systems resist common attacks. Configuration vulnerability management, default configuration versioning, and secure defaults documentation make sure secure configuration standards hold over time.
Why is configuration drift prevention key for default security monitoring and secure API defaults?
Configuration drift prevention makes sure systems don’t slide back into unsafe states. It works alongside default security monitoring, secure API defaults, and default secure session management. Default security alerts and default intrusion prevention help catch issues early, while secure default encryption keys and default security backup protect data.
How do secure default VPN config and secure default file permissions improve default security posture?
Secure default VPN config keeps connections private, while secure default file permissions stop unwanted access. Together, they strengthen the default security posture. Adding default authorization settings, default security automation, and default secure scripting helps systems maintain defense. Secure IoT defaults and default system lockdown lock things down even more.
How do secure default password policies and secure configuration standards tie into default SSL/TLS config?
Secure default password policies block weak logins and help users follow safer habits. These policies fit within secure configuration standards like default SSL/TLS config and secure config change control. Default secure environment variables, default security patching, and default secure coding practices round out a healthy security posture.
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Default_password
- https://wiki.centos.org/HowTos%282f%29Network%282f%29SecuringSSH.html

