
We’ve watched developers miss obvious security gaps because they never mapped where their data actually moves. Trust boundaries are the lines between safe and risky zones in an application, where a hacker might slip in if defenses aren’t there.
Spotting them requires looking at your own code with fresh eyes, seeing how information flows from one part to another. Our students learn this becomes foundational before anything else. One key difference between secure and vulnerable applications is whether trust boundaries have been identified and addressed.
Key Takeaways
- Trust boundaries are where security controls need to be strongest to prevent unauthorized access.
- Mapping system components and data flows helps reveal these critical boundaries.
- Enforcing secure coding practices and layered defenses at trust boundaries reduces risks significantly.
Understanding Trust Boundaries in Application Security
Trust boundaries in an application represent the invisible lines where one level of trust ends and another begins. For example, the boundary between an unauthenticated user browsing a website and the internal system that processes sensitive data. (1) These boundaries aren’t just theoretical, they mark where security assumptions shift, and where the risk for attacks like injection or privilege escalation spikes.
In one case study we observed data flow between micro-services without defined trust zones, which enabled an external API to access internal data without proper controls. Once we identified these boundaries and applied secure coding practices, the problem was much easier to fix. It’s like drawing a map of safe zones and danger zones within your system.
What Exactly Is a Trust Boundary?
- A trust boundary is a dividing line in your system where data or control passes between components with different trust levels.
- On one side you have fully trusted elements like internal services or authenticated users.
- On the other side, untrusted or less trusted elements such as external users, third-party services, or untrusted inputs.
This shift in trust means that when data or commands cross this boundary, security measures must kick in to validate, authenticate, or encrypt.
Why Identifying Trust Boundaries Matters
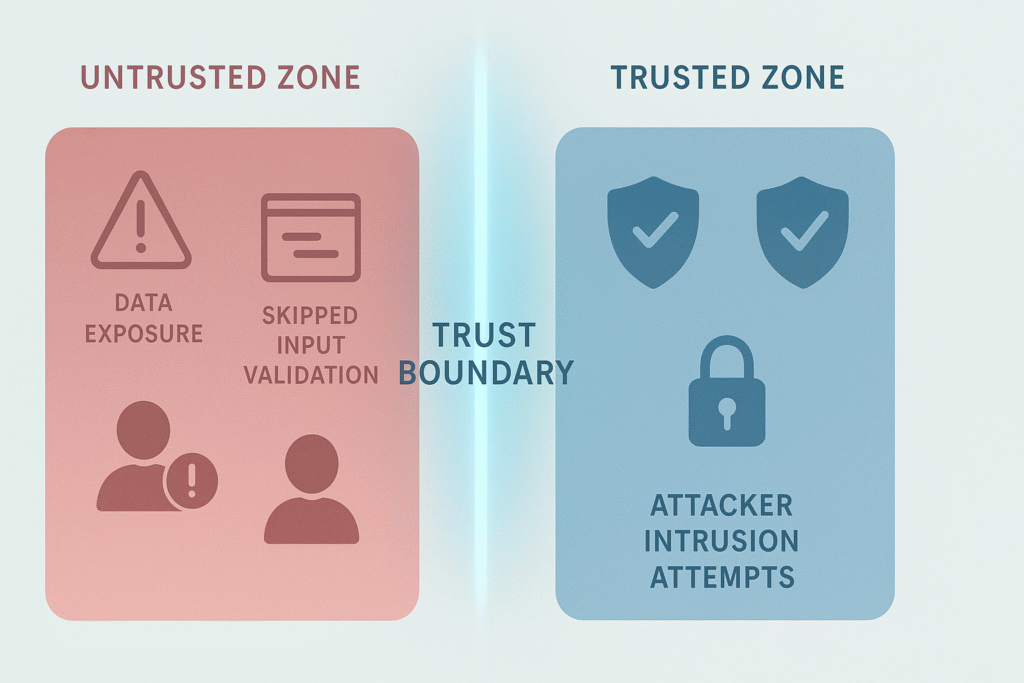
It’s tempting to think that security can be uniform across an application. But trust boundaries show us where that assumption breaks down. When these boundaries aren’t clearly identified: (2)
- Sensitive data might be exposed to untrusted users.
- Security controls like authentication or input validation might be skipped.
- Attackers can exploit integration points to escalate privileges or inject malicious commands.
From our experience, identifying trust boundaries early helped us understand where to focus secure coding efforts. It also shaped how we designed access control and encryption, making the whole system more resilient.
Why Focus on Trust Boundaries?
- They expose different data trust levels that require specific protections.
- Reveal interfaces vulnerable to attacks like spoofing or data leakage.
- Form the foundation for threat modeling and attack surface mapping.
- Help enforce secure communication across system components.
How to Identify Trust Boundaries
Breaking down trust boundaries into steps makes them manageable.
Step 1: Map Out Your System Architecture
Start by drawing out all components , services, modules, users, data flows. This visual helps understand where data moves and who touches it.
Step 2: Determine Trust Levels for Each Component
Assign trust ratings. Internal modules and authenticated admins usually count as trusted. External APIs or anonymous users fall on the untrusted side.
Step 3: Locate Interfaces and Data Entry/Exit Points
These are hotspots: user input fields, APIs, network connections, and third-party integrations. Wherever data crosses from outside to inside, a boundary exists.
Step 4: Identify Control Transitions
Look for where privileges change hands or where data enters from a lower-trust component into a higher-trust component.
Step 5: Document and Review
Keep diagrams and notes of trust boundaries. Sharing this with your security team or stakeholders ensures nothing’s missed.
In our work, this process revealed surprising boundaries , like an internal analytics tool that pulled data from an external source without proper validation. Fixing that gap was critical.
Key Points to Remember
- Trust boundary documentation aids in secure software development.
- It supports vulnerability management and boundary monitoring efforts.
- Regular reviews keep boundaries aligned with evolving system architecture.
Examples of Trust Boundaries in Applications
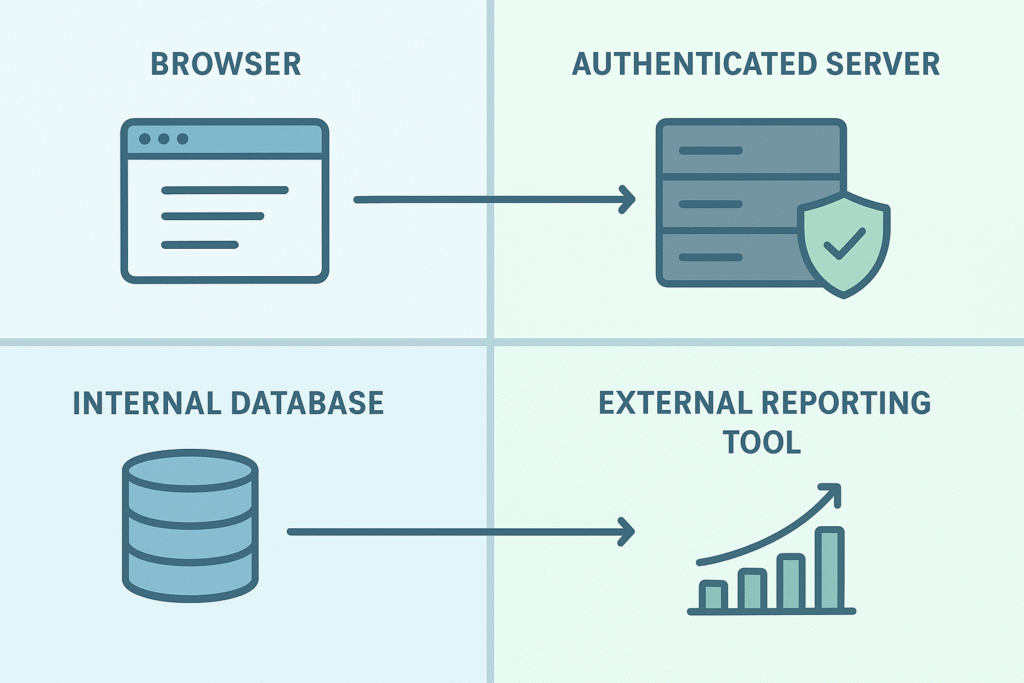
To make this more concrete, here are some real-world examples:
- Between a user’s browser (untrusted) and the authenticated web server (trusted).
- Between an internal database and an external reporting tool.
- Between a local network and the public internet.
- Between microservices handling sensitive data and those with general business logic.
Each of these boundaries represents a shift in trust assumptions requiring security controls.
Security Implications When Crossing Boundaries
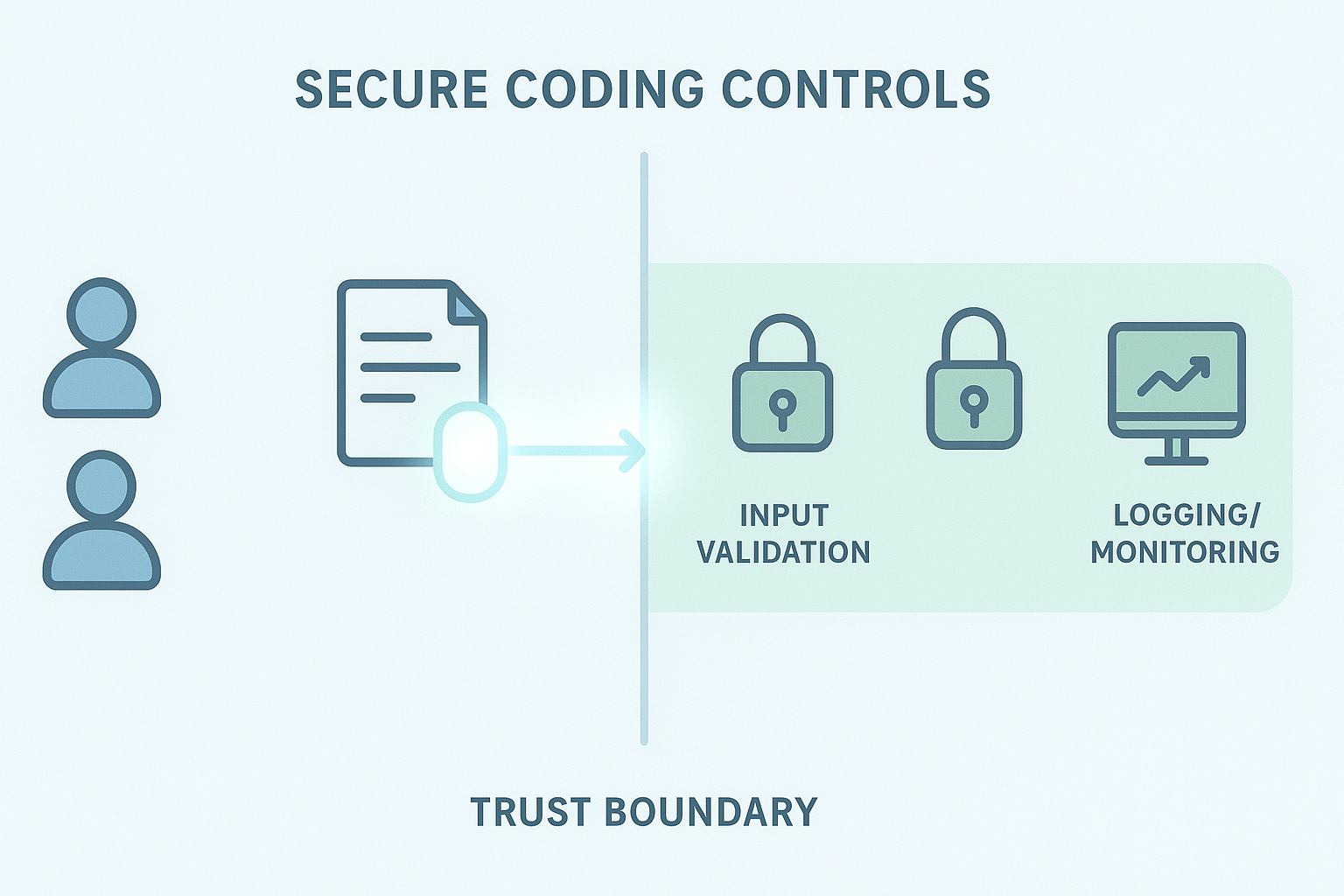
Crossing a trust boundary without proper protection invites trouble. That’s where secure coding practices come into play. We found enforcing these practices at boundaries can prevent many common vulnerabilities.
Here’s what to check when data or control crosses a trust boundary:
- Validate and sanitize all incoming data crossing a trust boundary; never trust input from lower-trust zones.
- Authentication and authorization checks: Confirm identities and access rights.
- Encryption in transit: Protect data from eavesdropping.
- Logging and monitoring: Track boundary crossings for audits and breach detection.
I recall a breach scenario where missing encryption on a boundary allowed attackers to sniff session tokens. After applying encrypted data transit and session management improvements, the risk dropped sharply.
Examples of Security Controls for Trust Boundaries
Examples of controls at trust boundaries include multi-factor authentication, network segmentation/firewalls, API gateways, privileged access management, and data-leakage prevention.
By layering these controls, we reduced the attack surface and bolstered defense in depth.
Best Practices for Securing Trust Boundaries
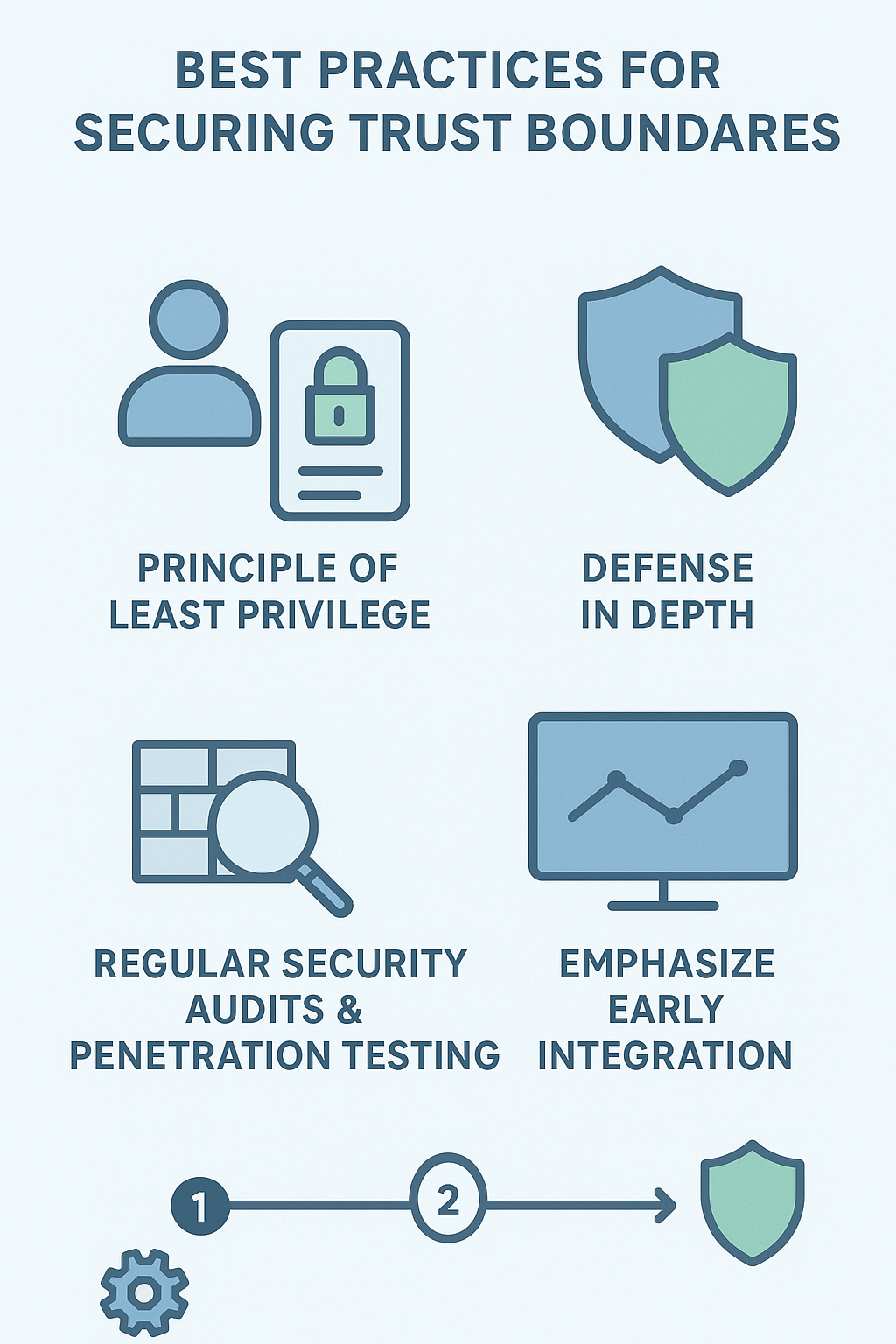
From our hands-on experience, blending secure coding practices with architectural strategies works best.
We also pay close attention to how teams are defining and managing trust boundaries, ensuring each division of the system is treated with the right isolation level.
Principle of Least Privilege
Limit access rights to the minimum necessary. This restricts damage if a boundary is breached.
Defense in Depth
Use multiple, overlapping security controls so that if one fails, others catch threats.
This becomes even more important when addressing what trust boundaries mean for overall boundary security, since different layers require different protective measures.
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Testing boundary defenses uncovers weaknesses before attackers do.
Such tests help in securing boundary crossings effectively, especially in paths where data moves between components with different trust levels.
We always advocate embedding these practices early in development, so trust boundaries aren’t afterthoughts but built-in safeguards.
FAQ
How do I know where trust boundaries exist in my app?
You can spot trust boundaries by looking at data trust levels, security zones, and points where trusted vs untrusted data meet. Check places where users send input, where microservices trust changes, or where cloud security boundaries shift. Many teams use threat modeling, trust boundary mapping, and system component trust reviews to see trust level transition more clearly.
What should I check first when reviewing data flow security?
Start with input validation and input sanitization at each access control point. Then look at cross-boundary data validation, API trust boundary checks, and secure communication paths. You should also watch for third-party integration risk, user roles separation, and application layers separation. These checks help keep trusted source verification simple and spot early trust boundary detection issues.
How can I reduce risks at authentication boundaries?
Look for identity verification points, user authentication zones, and authorization points where user access changes. Use multi-factor authentication boundaries, session management, and privileged access management to limit mistakes. Many developers add firewall segmentation, network isolation, and endpoint security to shrink the attack surface. These practices help prevent privilege escalation protection failures.
What helps keep external vs internal network areas safer?
Use secure network design, network segmentation, perimeter defense, and secure access points to keep traffic clean. Add encrypted data transit, data integrity checks, and secure API gateways. Cloud application boundaries also help manage trust boundary challenges. When you mix boundary monitoring and breach detection with access restriction policies, you strengthen threat surface reduction across your app.
How can I maintain application security as my system grows?
As you scale, watch for cloud components trust changes, service mesh security needs, and microservices trust gaps. Update security controls, security policy enforcement, and vulnerability management often. Many teams add malware containment, secure coding habits, and secure software development steps. Trust boundary visualization, trust boundary documentation, and secure data exchange help keep security framework integration smooth.
Conclusion
Identifying trust boundaries isn’t just a technical checklist, it’s a mindset that reshapes how we approach application security. When we understand where trust shifts inside a system, we gain control over where to apply secure coding practices, access controls, and encryption.
For anyone serious about reducing vulnerabilities and strengthening defenses, mapping and managing trust boundaries should be a priority. It protects sensitive data, limits privilege escalation, and reinforces a strong security framework.
If you’re building or maintaining applications, assess and document your trust boundaries, then apply the right controls at those transition points. And if you want structured, hands-on training to sharpen these skills, the Secure Coding Practices Bootcamp is a solid next step, practical, expert-led, and built for real developers.
References
- https://moxso.com/blog/what-is-a-trust-boundary
- https://cwe.mitre.org/data/definitions/501.html

