
Security isn’t some one-and-done fix – we’ve learned this lesson the hard way. Think of defense in depth like those old medieval castles with moats, walls, and guard towers. Each security layer backs up the others, kinda like having backup plans for your backup plans.
Our training shows developers how physical security (yes, those boring door locks), tech safeguards, and solid processes work together. When one defense fails, and trust me it will, the others step up.[1]
Key takeaway
- Security breaks at the weakest spot – usually where someone forgot about locks and doors.
- Good security’s like an onion, lots of layers make it work.
- Tech stuff’s great but don’t forget the basics – locked doors, smart staff, and knowing what to do when things go bad.
What are Physical Controls in Defense in Depth Cybersecurity?
The smartest coders in class don’t always think about who’s walking past their computers. Physical security often gets ignored until someone strolls into a restricted area – and by then it’s too late. A perfect firewall configuration means absolutely nothing when an outsider plugs something nasty right into a server.
Every serious data center needs those essential physical barriers. Decent security guards (not the sleepy ones) checking IDs, video surveillance covering the blind spots, and access logs that someone actually reads. Sure, digital security’s crucial, but you can’t ignore the real-world stuff.
Which Physical Controls Protect Systems from Unauthorized Access?
- Guards who watch the doors instead of their phones
- Heavy-duty doors with actual locks (skip those cheap office handles)
- ID systems that do more than look pretty
- Working cameras with people watching the feeds
Some companies learned this stuff the hard way. We’ve seen places where a delivery person wandered right into the server room – nobody stopped them. That’s why our training always starts with the basics. Physical security isn’t exciting, but it’s what keeps the bad guys from walking right in.
How Do Physical Controls Complement Other Security Layers?
You can’t hack what you can’t reach. Our students often focus on writing secure code, but we remind them – someone walking into your server room with a thumb drive bypasses all that careful coding. Physical security isn’t glamorous, but it’s like the foundation of a house.
When we visit clients with weak physical controls, we usually find other problems too. Good locks and watchful eyes let the tech team focus on stopping cyber threats, not worrying about who’s wandering around the building.
What are Administrative Controls in Defense in Depth Cybersecurity?
You can lock every door and write perfect code, but people still mess up. Administrative controls sound boring – they’re just rules and procedures – but we’ve watched solid companies get hacked because someone shared a password or skipped an update. These controls basically tell everyone “here’s how not to get us hacked.”
How Do Security Policies and Procedures Guide Organizational Security?
Good security policies aren’t just paperwork collecting dust. Our students learn that clear rules about password changes and spotting sketchy emails actually stop most dumb mistakes. Sure, nobody likes changing passwords every 90 days, but it beats explaining to the boss why customer data got leaked.
How Does Employee Training Enhance Security Posture?
Getting phished sucks – we know because we’ve seen entire networks go down from one clicked link. That’s why we run phishing tests in our training. One client’s click-rate on fake phishing emails dropped from 60% to 15% after our program. Sometimes the best security tool is just teaching people what bad stuff looks like.
What Role Does Vendor Risk Management Play in Supply Chain Security?
Trusting vendors blindly is asking for trouble. We teach developers to treat third-party code like a stranger’s USB drive – check it twice, then check it again. One company we worked with got ransomware through their HVAC vendor’s remote access. Now they review every vendor’s security, no exceptions. Sometimes the weakest link isn’t even in your building.
What are Technical Controls in Defense in Depth Cybersecurity?
Everyone loves the fancy security gear – those blinking lights and sleek interfaces sure look impressive. During our bootcamps, new students practically drool over the latest firewalls, but they’re missing what really matters.
Our instructors see it every week: someone drops fifty grand on security tools while their admin password sits on a Post-it note. Happens more than you’d think, even at big companies that should know better.
The technical stuff matters – no question there. But throwing money at expensive systems won’t fix bad habits. I had a client last month who bought top-shelf everything, then got hacked because someone left their workstation unlocked during lunch.
These things happen when people forget the basics we teach in week one: good security’s about the small stuff, not just the expensive toys collecting dust in the server room.
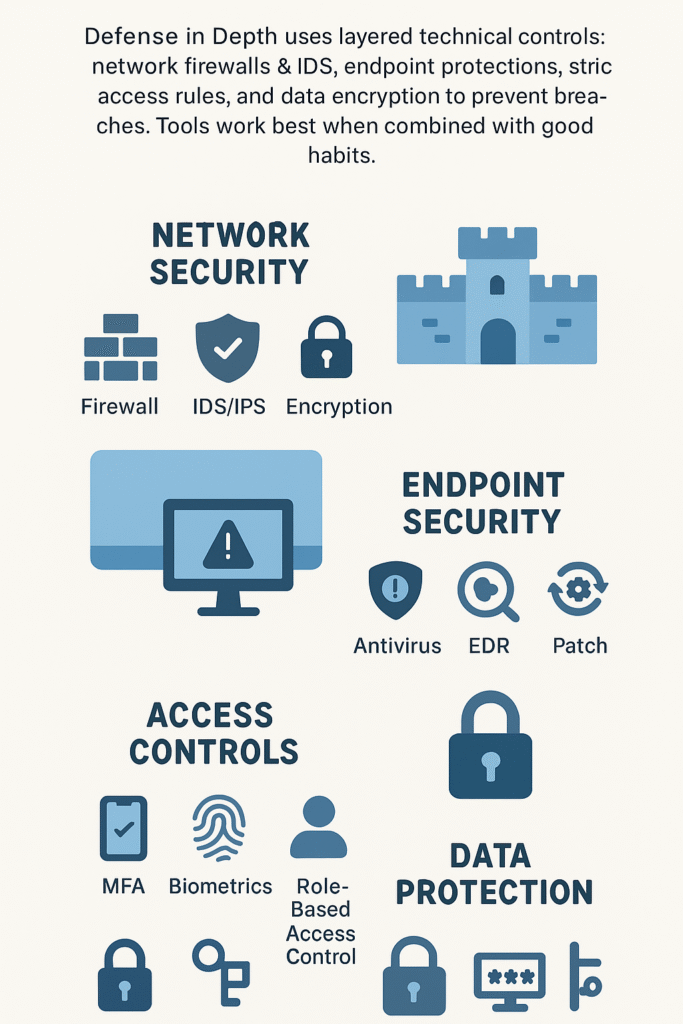
How Does Network Security Prevent and Detect Cyber Threats?
Networks need layers, like those old medieval castles. Firewalls create the first line of defense, keeping sketchy traffic where it belongs – outside. But one wall isn’t enough anymore, not with today’s threats. Last month a client called in panic mode – their “unbreakable” firewall got breached because they skipped intrusion detection. We had to clean up that mess for weeks.
The best security setups use everything: firewalls, IDS/IPS, encryption, the works. Some companies think one good tool’s enough – we see that mistake in almost every class we teach. Then they call us after hours when ransomware’s locked up their systems. Better to layer those defenses before something breaks, not after.
How Does Endpoint Security Safeguard Devices from Malware and Exploits?
Endpoints (that’s fancy talk for computers and phones) are like doors and windows – they’re where the bad guys usually break in. We teach our students to use:
- Antivirus that actually works (not the free stuff)
- EDR tools that spot weird behavior
- Regular patches – skip these and you’re asking for trouble
Last month, a company called us after ransomware hit. Turns out they’d skipped patches for six months. The kicker? Their EDR caught it early, but nobody was watching the alerts. Tools only work when someone’s paying attention.[2]
How Do Access Controls Regulate User Permissions and Authentication?
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) adds an extra verification step beyond passwords.
- Biometrics verify identities through fingerprints or facial recognition.
- Role-Based Access Control limits permissions based on job functions.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) secure remote access.
We implemented MFA across our organization after a credential theft incident. It drastically reduced unauthorized logins and is now a non-negotiable layer in access control.
How Does Data Protection Secure Sensitive Information?
- Encryption scrambles data at rest and in transit, making it unreadable without keys.
- Password hashing protects authentication credentials.
- Secure transfer protocols maintain data integrity during communication.
Data encryption is like locking files in a safe. Even if stolen, encrypted data remains useless. I’ve seen this protect companies from serious breaches.
What Application Security Measures Protect Against Web-based Attacks?
- Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) block common exploits such as cross-site scripting (XSS) and cross-site request forgery (CSRF).
WAFs act as gatekeepers for web apps, filtering malicious requests before they reach the server. They’ve been essential in preventing attacks on public-facing sites I’ve worked with.
How Do Monitoring and Analytics Detect Abnormal Cyber Activities?
- Continuous security monitoring keeps an eye on all systems.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) looks for unusual patterns that might signal insider threats or compromised accounts.
In one case, UEBA alerted us to an employee’s abnormal access pattern, leading to uncovering a phishing attack early.
How Does Incident Response Minimize Impact of Security Breaches?
- Incident Response Plans (IRP) lay out steps to contain and remediate breaches.
- Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) tools accelerate the response process.
Having a practiced IRP made a big difference during a ransomware attack I encountered. The team knew exactly what to do, minimizing downtime and data loss.
How Do Layered Security Examples Illustrate Defense in Depth Implementation?
To really understand implementing defense in depth, it helps to see how layers come together in specific scenarios.
What Comprises Website Protection Layers?
- Antivirus and anti-spam filter incoming traffic and emails.
- WAFs block application-layer attacks.
- Privacy controls protect user data.
- User training reduces risks from social engineering.
We combined these to protect a high-traffic website. The layered approach stopped phishing attempts and kept user data safe.
How Do Network Security Layers Work Together?
- Multiple firewalls at the perimeter and internal network segments.
- Encryption securing data moving across the network.
- Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) stopping threats detected in real time.
Strong network defense in depth layers combine multiple firewalls, encryption, and intrusion prevention systems to stop threats in real time.
How Does Endpoint Defense Protect User Devices?
- Antivirus scanning for known malware.
- Zero-day threat mitigation addressing unknown vulnerabilities.
Endpoint protection platforms (EPP) equipped with these features became our frontline defense for laptops and servers.
How Does Data Security Limit Exposure to Sensitive Information?
- Encryption prevents unauthorized access.
- Limiting data storage locations to reduce attack surfaces.
- Access restrictions controlling who can view or modify data.
By limiting where sensitive data lived and who could access it, we reduced the risk of accidental or malicious exposure.
How Does Defense in Depth Cybersecurity Strategy Reduce Overall Risk?
Credit: Cybersecurity Dojo
One of the main reasons a defense in depth security strategy works is because it doesn’t rely on a single control, each layer backs up the others. Each layer backs up the others. Even if one control fails, others stand ready to catch the threat.
Why Does Multiple Layer Redundancy Block Attack Progression?
Think of it like this: a firewall might stop most external attacks, but if something slips through, endpoint security or access controls can catch it next. This redundancy means attackers need to bypass several different types of controls, which gets harder with each layer.
How Does Defense in Depth Address People, Processes, and Technology?
It’s not just technology. Policies and training target human error and insider threats. Procedures ensure consistent, secure operations. Technology defends the digital assets. Together, they create a comprehensive shield.
How Has Military Strategy Influenced Defense in Depth Cybersecurity?
The concept borrows from military layered defense tactics, where multiple lines of defense slow or stop an enemy’s advance. Organizations with advanced threat environments have adapted these principles to cybersecurity.
What Emerging Technologies Enhance Defense in Depth Models?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning improve threat detection accuracy by analyzing vast data for unusual patterns. Automated response frameworks reduce incident resolution times, making the layers smarter and faster.
Conclusion
Defense in depth works, we see the proof every day in our training sessions. Smart security isn’t about picking one perfect solution, it’s about building layers that work together. Physical security, solid policies, and tech tools all need to mesh. Different companies need different combinations, but they all need multiple lines of defense.
When the layers work together, attackers have to work harder, and security teams get the time they need to spot and stop threats. Join our bootcamp to learn how to put defense in depth into action.
FAQ
What is defense in depth and how does it work in cyber security?
Defense in depth means building many walls instead of trusting just one. In cyber, it looks like layered security where multi-layer security shields systems at every level. A company might use firewall protection, an intrusion detection system, and an intrusion prevention system together. Add endpoint security with antivirus software or EDR tools for backup. Multi-factor authentication, IAM controls, and PAM help lock down access. Even simple security policies or security awareness training matter. The idea is to stop threats early, slow attackers down, and give teams time for cyber attack mitigation.
How does network security benefit from multi-layer security tools?
Network security is never just one lock on one door. A secure network often combines perimeter security, firewall protection, network segmentation, and a virtual private network. Cyber resilience grows when you add application security, a web application firewall, patch management, and vulnerability assessment. Endpoint detection and response or EPP tools watch devices. MFA and IAM restrict weak entry points. Security monitoring, threat detection, and UEBA alert teams to unusual actions. Together these layers create security breach prevention. Whether the threat is ransomware defense, malware protection, or insider threat protection, multi-layer security helps buy time and limit damage.
Why do organizations need zero trust security and strong access control?
Old trust models don’t work anymore. Zero trust security and zero trust architecture assume attackers may already be inside. That means tighter access control, stronger IAM, and sometimes biometric authentication. Privileged access management and PAM solutions help limit what sensitive accounts can do. Secure gateways and password hashing add strength. Data encryption and secure protocols keep encrypted data safe in motion. A security framework should also include DLP, cloud security, and SaaS security. When paired with user behavior analytics, insider threat protection, and threat hunting, zero trust reduces risks while boosting cyber hygiene and resilience.
How can teams prepare an incident response plan for cyber threats?
No one can stop every attack, so an incident response plan, or IRP, is critical. It guides cyber incident management, digital forensics, and cyber attack mitigation after a breach. Security operations center teams may use SOAR, security orchestration, and security automation to speed response. Security alerts, threat intelligence, and machine learning security tools help catch problems early. AI in cybersecurity can support faster decisions. An IRP should cover ransomware defense, malware protection, and APT defense. Regular security awareness training keeps people sharp. With strong cyber resilience, even advanced persistent threats don’t mean total disaster.
What role do supply chain security and compliance play in defense in depth?
A secure network is only as safe as its weakest link. Supply chain security and vendor risk management matter as much as firewall protection or VPNs. Security compliance, compliance audits, and following a strong security framework help prove defenses are in place. Security policies, cyber hygiene, and security awareness training reduce careless mistakes. Security architecture should include secure gateways, cloud security, and application security for SaaS platforms. Cyber resilience depends on patch management, network traffic analysis, and threat detection. Strong security breach prevention comes from combining PAM, DLP, threat hunting, and oversight from a security operations center.
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swiss_cheese_model
- https://www.enisa.europa.eu/publications

