A natural language prompt is simply a clear question or instruction written in everyday English. We use prompts constantly in our secure-development bootcamp, and many of us learned firsthand that clarity, not fancy terms, shapes the quality of an answer.
When someone writes vaguely, the response drifts; when they write with intent, the output stays sharp and useful. Over time, our team has seen how thoughtful prompts help learners think through problems, not just generate text. This guide walks through that process step by step, keep reading to sharpen how you communicate.
Key Takeaways
- Be specific and clear in your instructions.
- Provide context and examples when needed.
- Structure complex requests as a series of simple steps.
Starting with the Basics
We often start with something simple, like asking for a summary. “Summarize this article,” you might type. That’s a zero-shot prompt. You’re giving the AI a task with no examples, hoping its training is enough. Sometimes it works perfectly. Other times, the summary is too short, or it misses the main point. This is where you learn your first lesson. The AI needs more from you. It needs a nudge in the right direction.
That nudge often comes in the form of an example. This is few-shot prompting. You show the AI what a good answer looks like. For instance, if you want it to extract key dates from a historical text, you might provide one example first. “Text: The company was founded in 1998. Key Date: 1998.”
Then you give it the new text. This tiny bit of guidance dramatically improves the accuracy. It’s like showing a new employee a sample of the work you expect, very similar to how beginners get comfortable when they first explore vibe coding and start translating ideas into simple, workable instructions. Studies show that adding just one or two examples can raise task accuracy by 10–30 percentage points, especially for classification or extraction tasks where context matters. (1)
- State the task clearly and directly.
- Provide one or two examples of the desired format.
- Then present your new request.
The Power of Thinking Step by Step
Credits: Simplilearn
Some questions are just too big. “Explain the economic causes of World War II,” is a massive request. The AI might produce a dense, confusing paragraph. This is where chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting shines. You ask the AI to reason aloud. The instruction “Explain the economic causes of World War II, thinking step by step,” forces a different kind of output. The AI breaks the problem down.
It might start with the Treaty of Versailles, then move to hyperinflation, then global depression. You get a logical progression instead of an information dump. In fact, research on chain-of-thought prompting found that a simple cue like “think step by step” can boost reasoning accuracy from 17.7% to 78.7% on benchmark tasks. (2) This technique is invaluable for complex reasoning, coding problems, or anything that requires a structured argument. It makes the AI’s process visible, which also makes it easier for you to correct or guide.
The single most important principle is specificity. Vague prompts get vague answers. “Write something about marketing,” will generate generic fluff. “Write a 150-word email for a SaaS product marketing to small business owners, focusing on time-saving features,” gives the AI a target. You’ve defined the format (email), the length (150 words), the audience (small business owners), and the topic (time-saving features).
The more constraints you provide, the less room the AI has to hallucinate or go off-topic. It’s not about being restrictive, it’s about being clear. You are the director, and the prompt is your script. You can also guide readers to a practical example by pointing them to the best first project for Vibe coding, which shows how beginners can start small and build confidence quickly.
Giving the AI a Role to Play
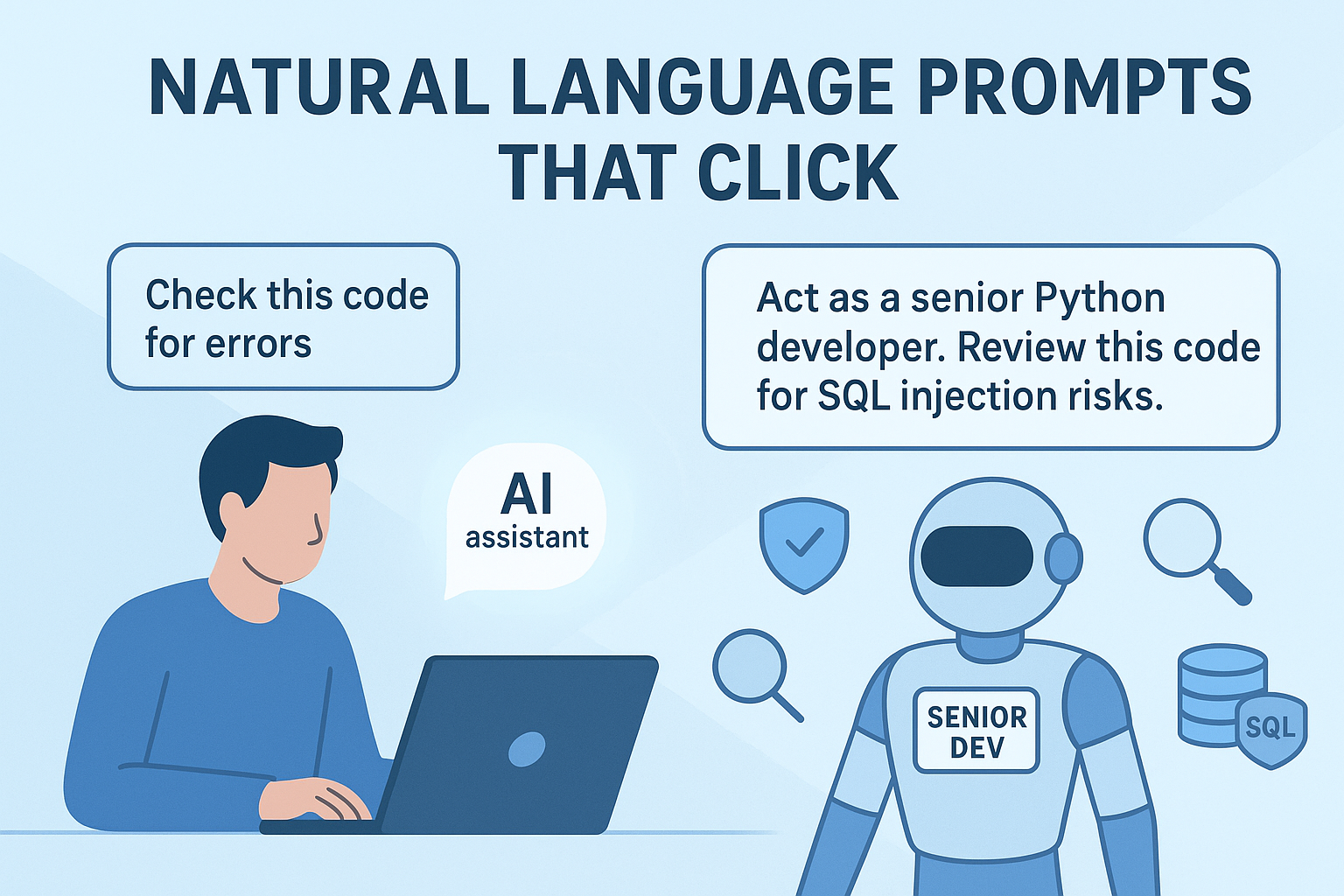
Context is the secret ingredient. Imagine asking a friend, “What should I do?” It’s an unanswerable question. But if you say, “I have a meeting with my boss tomorrow to ask for a raise, what should I do?” now they can help. AI is the same. A prompt like “Check this code for errors” is weak.
“Act as a senior Python developer. Review this code snippet for security vulnerabilities, specifically looking for SQL injection risks,” is powerful, especially for people learning to shape clearer instructions while getting used to ai-assisted workflows. You’ve given the AI a role, a specific task, and a domain of focus. This contextual framing narrows the AI’s attention to what truly matters to you.
Building a Conversation
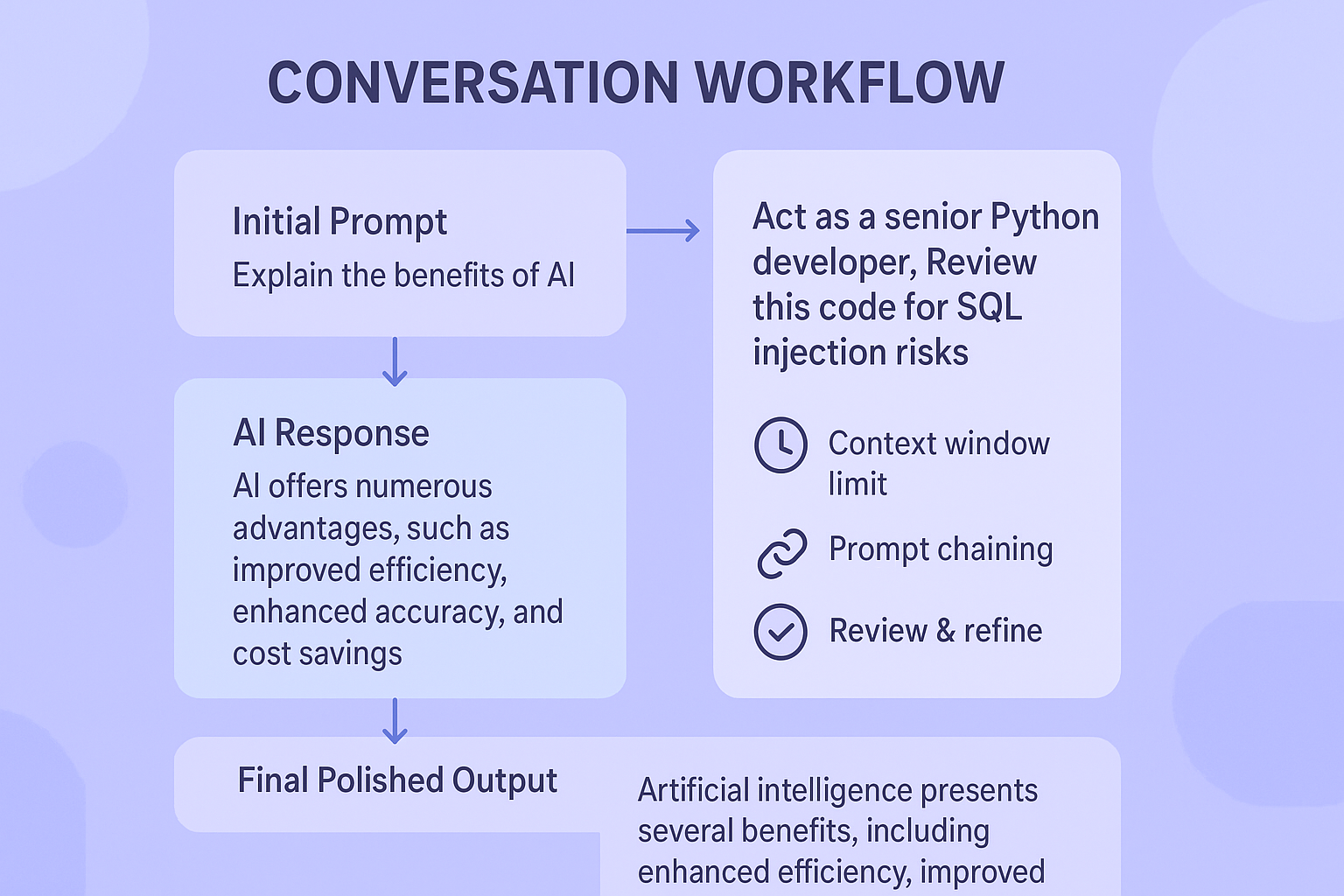
Prompting is rarely a one-and-done affair. It’s a conversation. Your first prompt might not be perfect. The output might be close, but not quite right. This is where iterative prompting comes in. You don’t start over. You refine. Based on the AI’s response, you give a follow-up instruction. “That’s good, but make the tone more formal,” or “Now, rewrite that same point but for a beginner audience.”
This iterative process is how you hone in on the perfect output. It’s a collaboration. The AI generates, you critique and guide. This back-and-forth is where much of the real magic happens, transforming a rough idea into a polished final product.
You also have to think about the AI’s limits. These models have a “context window,” a maximum amount of text they can consider at once. If your prompt is too long, it might get cut off. It’s like trying to have a conversation in a very noisy room, only the most recent words are heard clearly.
This is why being concise in your initial instructions matters. For very long tasks, you might use prompt chaining, breaking the work into a sequence of smaller, self-contained prompts. Each step feeds into the next, keeping the context manageable for the AI and ensuring a coherent final result.
- Review the AI’s initial output carefully.
- Provide clear, specific feedback for the next iteration.
- Break extremely long tasks into a sequence of smaller prompts.
Writing with Safety in Mind

Security is a dimension you must consider from the start. When you’re crafting prompts, especially for code generation or handling sensitive data, you have to build in safety. We use secure coding practices by being explicit about safety requirements in the prompt itself.
Instead of just “Write a login function,” a better prompt is “Write a secure login function in Python that includes password hashing and protection against brute-force attacks.” You are instructing the AI to prioritize security as a primary goal, not an afterthought. This proactive approach mitigates risk and leads to more robust outputs. It’s a fundamental part of responsible prompting.
FAQ
What makes natural language prompts feel unclear, and how can beginners fix that?
Clarity often slips when people rush their language model instructions or forget specificity in prompts. Beginners can steady things by adding a short task description, giving input data prompts, and naming the output format specification. Small tweaks—like role-playing prompts or adding context in prompts—help AI prompting stay simple, even when using LLM prompts for everyday tasks.
How can new users choose between zero-shot prompting, one-shot prompting, and few-shot prompting?
Beginners often wonder which option works best. Zero-shot prompting is fast, but one-shot prompting or few-shot prompting adds helpful hints. These small examples support in-context learning and reduce confusion. When users pair example-based prompting with prompt structure that highlights step-by-step reasoning, they usually get clearer results across translation prompts, text classification prompts, and sentiment analysis prompts.
What should someone do when an AI struggles with step-by-step reasoning?
When an AI gets stuck, beginners can try chain-of-thought prompting or CoT prompting to slow the model down. If that fails, iterative prompting or prompt chaining helps break problems apart. These tactics reduce hallucination and support bias mitigation in prompts. They also make advanced prompt techniques feel manageable, even for simple question answering prompts.
How can token limits in prompts affect the way users design creative or technical tasks?
Token limits in prompts shape how much detail fits into natural language generation tasks. Users often trim extra words, rely on concise prompt engineering, or break input into chunks. They can still use persona prompts, creative writing prompts, or code generation prompts by keeping prompt optimization simple. When needed, coarse-grained instructions help avoid overload while keeping the tone steady.
How can beginners stay safe when trying advanced ideas like system prompts or multi-agent prompting?
Safety prompts and alignment prompts guide beginners toward responsible AI prompting. People can build checks that reduce risky outputs, using jailbreak prevention, red-teaming prompts, or ethical AI prompting for balance. Even when experimenting with system prompts, user prompts, tool-augmented prompting, or retrieval augmented generation, simple ambiguity resolution and edge case handling keep things predictable without blocking learning.
Building Stronger Skills Through Better Prompts
Effective natural language prompts unlock the real power of AI: the ability to turn your ideas into clear, actionable outcomes. Whether you’re reasoning step by step, giving the AI a role, or tightening your instructions, the difference always comes from specificity and intent. We’ve watched this skill change how learners solve problems in our secure-development bootcamp, helping them think more sharply and build with more confidence. If you want to strengthen both your prompting and secure coding skills, the Secure Coding Practices Bootcamp is the next place to grow.
References
- https://www.emergentmind.com/topics/prompting-strategies
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.11916

