
You can absolutely write real code just by talking, and modern AI is finally good enough to make that practical. Instead of pecking at keys, you describe what you want, a function, a refactor, a test suite, and your tools translate that intent into working code.
This isn’t plain speech-to-text; it’s context-aware help that understands structure, style, and even your stack. When you set it up well, voice prompt coding feels less like dictation and more like pair programming. If you’re curious how to build that kind of setup for yourself, keep reading.
Key Takeaways
- Voice coding transforms natural speech into executable code through AI-powered transcription and interpretation.
- A quality microphone and proper software configuration are critical for achieving high transcription accuracy.
- The most effective approach combines high-level verbal descriptions with AI editors for context-aware code generation.
The Promise of Voice: Streamlining Coding Workflows
You sit down to code, and your hands feel tired before you even start. The repetitive strain of typing thousands of lines adds up. Voice coding offers a different path.
It’s about using your voice as the primary input, letting speech-to-text and AI do the heavy lifting. This isn’t just about accessibility. It’s a fundamental shift in how we interact with our development environment.
The core benefit is speed. When you can describe a function in natural language faster than you can type its syntax, you unlock a new level of productivity. This kind of vibe coding workflow keeps your creative flow intact because you’re focused on intent and logic, not keystrokes. You stay in the problem-solving zone.
In fact, in a global survey, “87% of developers now use AI tools regularly”, showing how widespread these tools have become in speeding up coding workflows. [1]
Your creative flow isn’t interrupted by the mechanical act of typing. You stay in the problem-solving zone. Ideas translate to code almost as fast as you can think them.
It also changes the nature of repetitive tasks. Instead of manually writing another boilerplate function, you just say, “Create a new React component for a user profile card.” The AI generates the structure. You then use verbal commands to refine it. This iterative, verbal loop keeps your momentum high.
Setting Up Your Voice Coding Environment: A Step-by-Step Guide
Your first step is choosing a tool. Some coding tools and editors have voice modes built directly in. These are often the easiest to start with because everything works in one place.
You press a hotkey, speak, and the editor transcribes and processes your command immediately. The integration is seamless.
Other approaches use system-wide dictation tools. These apps run independently of your code editor. You dictate into them, and they send the transcribed text to any application you choose, like your IDE. This method offers more flexibility but requires switching focus between applications.
Next, configure your microphone. This is more important than you might think. A standard headset mic can work, but a directional microphone that minimizes background noise will significantly improve accuracy. You want the software to hear your words, not your keyboard clicks or office chatter.
Finally, train the system. Most voice recognition software improves with use. Spend some time dictating code-specific vocabulary.
Say words like “async function,” “database schema,” and “environment variable.” The system learns your accent and your technical lexicon. This initial investment pays off in sputtered accuracy later.
| Tool Type | Primary Use Case | Key Consideration |
| Integrated Voice Mode | All-in-one coding and command execution | Easiest setup, less customizable |
| System-Wide Dictation | Flexibility across multiple apps and tasks | Requires app switching, highly versatile |
| Custom Macro Tool | Automating specific, repetitive actions | Best for power users with defined workflows |
Voice Prompts in Action: Practical Examples for Developers
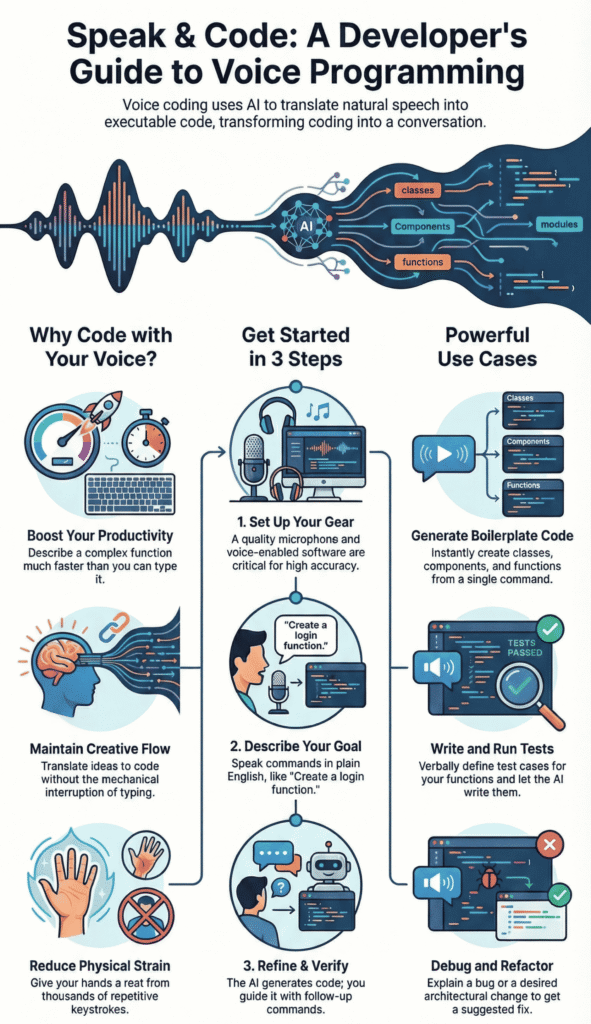
Let’s see how this works in a real scenario. Suppose you need to add user authentication to a web app. Instead of typing, you might say, “Create a login function that checks the email and password against the database. Return a JWT token if the credentials are valid.” The AI interprets this and generates the initial code block.
You notice it didn’t include input validation. Your follow-up prompt is verbal. “Now, add validation to ensure the email is in a valid format and the password is at least eight characters long.” The AI understands the context and amends the code accordingly. The entire process is hands-free.
Debugging becomes a conversation. You can say, “Look at the calculateTotal function. There’s a bug where the tax isn’t being applied to discounted items. Find the logic error and fix it.” The AI can analyze the code, pinpoint the issue, and suggest a correction. You guide it with your voice.
Refactoring is another powerful use case. “Refactor the dataProcessor class to use the strategy pattern for different file formats.” You’re describing the architectural change at a high level, and the AI handles the detailed code transformation. This allows you to focus on design, not syntax.
- Generating Boilerplate: “Create a new Python class for a customer with name, email, and phone number attributes.”
- Writing Tests: “Generate unit tests for the validateUserInput function covering valid and invalid cases.”
- Database Queries: “Write a SQL query to select all orders from the last 30 days and join them with the customer table.”
Voice Coding vs. Traditional IDEs: A Balanced Comparison
So, should you ditch the keyboard for good? Probably not. Most developers end up somewhere in the middle, using both voice and typing like two tools in the same toolbox instead of rivals.
Voice coding shines when you’re sketching out ideas and structure. It’s strong at:
- Rapid prototyping
- Laying out high-level architecture
- Building the rough skeleton of an app at surprising speed
You can outline classes, functions, and modules in minutes, then circle back to clean things up.
The keyboard still wins when you need precision. For tiny edits, tight control over syntax, or a one-line change, typing is often quicker and less awkward than speaking.
The real skill is learning when to switch: voice for broad strokes, keyboard for careful detail work.
AI integration adds another layer to this choice. Some tools are designed as AI-native from the start. They read across your whole codebase, track relationships between files, and handle complex refactors based on spoken instructions.
In those setups, your voice becomes more like a conversation with an assistant that understands your project as a whole. Then there are traditional IDEs with AI extensions bolted on. They’re strong at:
- Generating snippets in the current file
- Autocompleting patterns you use a lot
- Keeping you inside a familiar editing environment
They may not see across all your files as deeply, but they feel safe and known. So you’re often trading a bit of global intelligence for comfort and muscle memory.
Best Practices for Effective Voice Coding

Your success with voice coding hinges on how you speak. Clarity beats speed. Enunciate your words, especially technical terms. It’s better to say “create a new const variable” slowly and clearly than to mumble it quickly. The transcription accuracy will be higher, saving you time on corrections.
Use structured phrases. Learning how to write effective prompts makes a real difference here. Instead of a long, rambling sentence, break your commands into distinct parts. “Step one, import the axios library. Step two, write a function to fetch user data from the API endpoint.”
Research has found that developers “report that AI tools raise productivity by 10 to 30% on average”, when they use assistive tools for tasks like writing and testing code. [2] “Step one, import the axios library. Step two, write a function to fetch user data from the API endpoint.”
This chunking helps the AI parse your intent more accurately. It’s like giving the AI a clear outline.
Customization is your friend. Most tools allow you to create custom voice commands or macros. If you frequently write a specific code pattern, create a shortcut for it. You could set up a command so that saying “scaffold CRUD” generates all the basic Create, Read, Update, Delete functions for a given model.
Always verify the transcription. Before you hit “submit” to the AI, take a half-second to glance at the text your speech produced. Catching a typo like “fuction” instead of “function” at this stage prevents the AI from generating confused or erroneous code. This quick check is a crucial habit.
- Speak Clearly: Articulate each word, don’t rush.
- Pause Between Ideas: Give the parser a moment to catch up.
- Use Tech Vocabulary: Train the software on your stack’s terms.
- Review Before Sending: A quick scan of the transcription saves time.
We find that starting with Secure Coding Practices through voice commands sets a strong foundation. Instead of trying to remember every security rule, you can verbally enforce them.
Say something like, “Install this function and ensure all user inputs are sanitized to prevent SQL injection.” The AI can bake those best practices directly into the generated code. It’s a way to make security a default, not an afterthought.
Addressing Potential Concerns and Challenges

The biggest worry is accuracy. What if the software mishears you? It happens. You might say “list” and it hears “least.” This is why the verification step is non-negotible. With a good microphone and some training, error rates drop significantly. It’s a skill that improves with practice, like typing itself.
Privacy is another common question. Where is your code and voice data being processed? Some tools process everything locally on your machine, which is the most secure option.
Others use cloud services. It’s essential to understand the data handling policies of the tools you choose, especially for professional or sensitive projects.
There is a learning curve. Your first session with voice coding will feel awkward. You’ll speak too formally, or you’ll forget the right commands.
That’s normal. The key is to start with simple tasks. Try generating a single function. Then a class. Gradually work up to more complex operations. You’re learning a new interface.
Choosing the Right Approach for You

Most developers don’t pick one path forever, they shift based on what they’re building and how fast they need to move.
If speed is your main goal, a dedicated voice-coding environment can feel almost unfair. The way speech, AI, and the editor work together makes it easy to:
- Try ideas fast
- Reshape structure on the fly
- Keep momentum without stopping to type
You trade some familiarity for a very fluid loop between thought and code.
If you’re working inside a team with fixed tools, a voice dictation or AI extension on top of your current editor is usually calmer.
You keep your existing setup, your shortcuts, your plugins, and just layer voice on when it helps. That way, you gain productivity without forcing everyone to change how they work.
Then there are developers who want total control. For them, wiring up Python libraries, APIs, and custom scripts becomes its own project. It’s more effort upfront, but you can tune:
- Wake words and commands
- How transcripts are cleaned
- How AI responds to your codebase
That path demands more from you, but it can turn voice coding into something that feels built for your brain, not someone else’s idea of “standard.”
FAQ
How can I start hands-free coding using voice prompts effectively?
You can start hands-free coding by speaking clear natural language prompts that describe what you want the code to do.
Focus on voice code generation using simple, structured speech phrases. This builds a smooth speech-to-code workflow, reduces typing, and helps you stay focused while dictating function creation or navigating code verbally.
What’s the best way to improve transcription accuracy for voice coding?
To improve transcription accuracy, train your tech vocabulary and speak at a steady pace. Use pause-based parsing to separate ideas and give context-aware dictation.
Clear pronunciation and noise control help speaker-dependent models understand intent better, which leads to more reliable audio code editing and fewer corrections.
How do voice prompts help with debugging and refactoring code?
Voice prompts support hands-free debugging by letting you explain errors aloud and request fixes verbally.
You can use refactor speech commands to rename variables, simplify logic, or run verbal test commands. This keeps your creative momentum flowing while receiving real-time code feedback during the process.
Can voice prompts speed up coding for complex projects?
Yes, voice prompts can increase coding speed by letting you describe high-level logic instead of writing syntax.
Iterative verbal coding helps you prototype quickly, adjust ideas fast, and maintain an iteration verbal loop. Many developers use this approach to improve voice coding efficiency and reduce mental fatigue.
Is voice-based coding useful for accessibility and long sessions?
Voice-based coding supports accessibility programming by reducing strain from constant typing. It helps prevent repetitive stress injuries and supports longer sessions through dictation for developers.
By combining natural language prompts with hands-free workflows, you can code comfortably while maintaining productivity and focus over time.
Your Next Steps with Voice Coding
Voice prompt coding isn’t just a neat trick, it’s a real productivity boost that keeps your hands fresh and your brain in flow.
The tools are ready now, and they’re better than most people expect. Yes, it feels weird at first, but that fades fast. Start small: pick one tool, spend thirty minutes setting up your mic, and use your voice to write a simple function.
As you adjust, it stops feeling like dictation and starts feeling like a conversation with your code. Ready to push this further? Join the Secure Coding Bootcamp and sharpen how you build.
References
- https://www.elysiate.com/blog/ai-in-software-development-survey-2025
- https://www.index.dev/blog/developer-productivity-statistics-with-ai-tools

