
When it comes to conveying complex logic to AI, clarity is not just helpful, it’s essential. Many of us have faced the frustration of explaining intricate concepts, only to find the AI misinterpreting our intentions. This often occurs due to vague phrasing or overly complicated structures.
By breaking down logic into manageable steps, employing structured formats, and refining our prompts iteratively, we can significantly enhance the AI’s comprehension and responsiveness. In this guide, we’ll explore practical strategies to make our communications clear and effective, ensuring that our logic resonates with the AI’s reasoning capabilities.
Key Takeaways
- Clarity Matters: Break down complex logic into simple, structured steps to enhance AI comprehension.
- Utilize Structured Formats: Use pseudocode or flowcharts to present logic in a clear, organized way.
- Iterate and Validate: Continuously refine prompts by asking the AI to rephrase and clarify its understanding.
Understanding the Challenge
Why Clear Logic is Crucial for AI
When we try to explain complex logic to an AI, every unclear step becomes a problem. If our reasoning is messy, the AI can’t follow it well and may give answers that sound right but miss the point. Clear, simple structure helps the AI stay on track and support real decisions, not just generate text. Strong prompt clarity reduces confusion early and keeps reasoning aligned from the first instruction to the final output.
To make logic easier for AI to follow, it helps when we:
- Break ideas into small, ordered steps
- Use consistent terms throughout
- Avoid vague words and mixed conditions
When we do that, the AI responds in a way that feels closer to what we actually meant.
Key Concepts in AI Reasoning
AI uses different reasoning methods, and knowing the basics changes how we talk to it. Rule-based systems follow explicit “if–then” rules, so they rely on precise conditions. Neural networks learn patterns from data, so they respond better to clear examples and consistent phrasing.
By understanding how each type handles information, we can shape our logic so the AI is less likely to misread it and more likely to support the work we’re actually trying to do [1].
Step-by-Step Guide to Describing Logic

Step 1: Break Down Complex Logic
When logic is dense, we start by splitting it into small, clear moves. Take a net present value (NPV) calculation:
- List all cash flows (CF).
- Set the discount rate for each cash flow (r).
- Calculate the present value (PV) of each CF using its rate.
- Add all PVs to get the final NPV.
This kind of breakdown matches how AI follows chained reasoning, one step at a time.
Step 2: Use Structured Formats
Formats like pseudocode, flowcharts, or JSON make logic easier to follow, both for humans and AI. These structures are a core part of effective prompting because they remove guesswork and show the AI exactly how decisions should flow. A JSON-style rule might look like:
json
{
“if”: “cash flow > 0”,
“then”: “calculate present value”,
“else”: “not applicable”
}
Clear structure cuts down on guessing.
Step 3: Incorporate Examples and Constraints
Examples tie the logic to something concrete. For instance:
Input: CF = [1000, 2000, 3000], r = [0.05, 0.07, 0.09]
Output: a single NPV value.
Constraints like “use integer values only” keep the AI from wandering into side cases you do not want. Testing edge cases, such as negative cash flows, helps catch gaps early.
Step 4: Refine with Iteration and Validation
We can ask the AI to restate the logic in its own words. If the answer sounds off, we adjust the steps, tighten the wording, and try again.
| Step | Action Description | Purpose for AI Understanding |
| Step 1 | Identify all variables and inputs | Prevents missing or assumed data |
| Step 2 | Define rules or calculations clearly | Ensures correct logical processing |
| Step 3 | Apply rules in a fixed order | Supports step-by-step reasoning |
| Step 4 | Combine results into final output | Aligns AI response with expected result |
Tailoring Logic to Different AI Models

Rule-Based Systems
With rule-based AIs, logic needs to be clear, tight, and explicit. Each rule should show how a condition leads to an outcome, without guesswork. For example, in a legal setting, we might spell out statutory requirements as a set of direct rules the system can follow.
Helpful habits for rule-based logic:
- Use “if–then–else” structures.
- Keep conditions precise, not vague.
- Avoid overlapping or conflicting rules.
This makes the system easier to check and update.
Neural Networks
Neural networks work differently. They learn from patterns in data instead of hand-written rules. So when we describe logic for them, we lean more on examples and relationships than strict formulas [2].
To guide a neural model, we might:
- Provide clear input–output pairs.
- Highlight which variables matter most.
- Set constraints like “assume all data is numeric.”
By focusing on patterns and boundaries, we help the model learn the behavior we actually care about, instead of leaving it to guess what matters.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
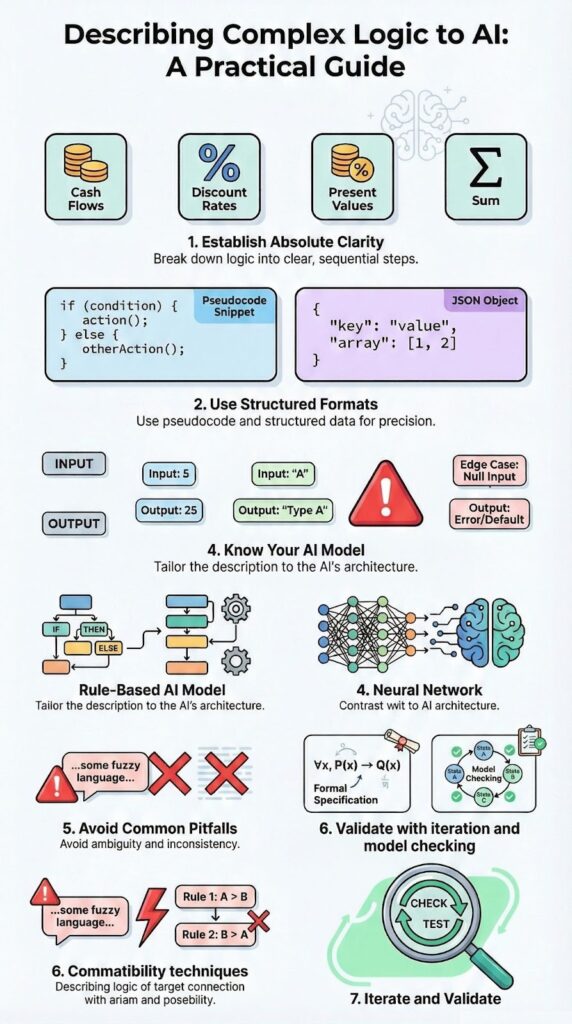
Ambiguity and Misinterpretation
When we describe logic to AI, vague language is one of the main problems. If a prompt is too wordy or tries to do too many things at once, the model has to guess what we really want. Learning how to write effective prompts helps reduce ambiguity by keeping instructions focused, scoped, and technically precise. That’s usually where mistakes begin.
To cut down on confusion, it helps to:
- Use simple, direct sentences
- Ask for one clear task at a time
- Avoid fuzzy terms like “a bit,” “roughly,” or “kind of”
Straightforward wording makes the logic easier for the AI to follow.
Inconsistent Logic
Another quiet problem is logic that changes halfway through. If rules don’t line up or definitions shift, the AI may produce answers that feel random, even if the prompt looks detailed.
Regular checks can help, such as reviewing:
- Whether the same term always means the same thing
- Whether two rules contradict each other
- Whether edge cases are handled in the same style
Catching these breaks in logic early keeps errors from spreading deeper into the project.
Advanced Techniques
Credits : Learning To Code With AI
Formal Specification Languages
When logic gets complex or safety-critical, informal notes usually are not enough. Formal specification languages help us describe systems in a strict, mathematical way, so there is less room for doubt or mixed meaning.
They are useful when we want to:
- Define clear rules and constraints
- Describe states and valid transitions
- Make sure every part of the system follows the same structure
This kind of precision gives both humans and AIs a shared, stable reference.
Model Checking
Model checking is a method to see if the logic we designed actually behaves as intended. Instead of trusting a description on paper, we compare the AI’s behavior against a formal model.
In practice, this means we:
- Build a model of the system’s possible states
- Define properties we want to always hold (for example, “no invalid state is reachable”)
- Use tools to automatically check if the model ever breaks those properties
If the checker finds a problem, we get a concrete example of where the logic fails, which makes it easier to fix before deployment.
FAQ
How can structured prompting help explain complex logic to an AI clearly?
Structured prompting explains complex logic by organizing instructions into clear, ordered parts. You explicitly define variables, constraints, and expected outputs before asking the AI to reason. Using logic decomposition, step-by-step reasoning, and input output examples reduces ambiguity. This approach improves large language models reasoning and helps prevent misunderstandings caused by vague natural language.
When should I use pseudocode or flowcharts instead of plain language?
You should use a pseudocode explanation or flowcharts text when logic includes conditions, loops, or multiple decision paths. These formats clearly show conditional branching prompts, iterative algorithms, and recursion descriptions. They also make state transitions and decision trees AI easier to follow, which improves accuracy and supports consistent reasoning.
How do examples improve AI understanding of complex decision logic?
Examples turn abstract rules into concrete behavior. Input output examples and few-shot examples show exactly how logic should work in real cases. They clarify edge case handling, boolean expressions, and rule boundaries. Well-chosen examples reduce ambiguity, support constraint specification, and help symbolic logic AI follow decisions without guessing missing steps.
What is the best way to describe multi-step or recursive processes?
Describe multi-step logic in a clear sequence using step-by-step reasoning. Break the process into smaller functions with clear roles using function decomposition. For recursion description, define the base case and the repeating rule. This structure helps explain finite state machines, graph traversal logic, and backtracking algorithms without confusion.
How can I reduce errors when explaining advanced logic concepts to AI?
Reduce errors by writing precise instructions and avoiding implied meaning. Define every variable, rule, and constraint clearly. Use validation rules and verification prompts to check logic consistency. Applying ambiguity reduction and self-consistency check methods ensures the AI follows your intended logic instead of filling gaps with incorrect assumptions.
Building a Secure and Responsible Logic Framework
Secure Coding Practices can serve as our foundational approach, providing a framework that supports all layers of logic. By emphasizing security in our coding interactions, we contribute to a culture of responsibility in AI development, maintaining data integrity while still leaving room for real innovation in complex problem-solving.
With these strategies in mind, we can foster a more productive dialogue with AI systems, making it easier for them to operate with clarity, accuracy, and clear alignment to the tasks at hand. If you want to turn these ideas into daily practice, the Secure Coding Practices Bootcamp offers a focused, hands-on way to learn secure coding with real code, real labs, and practical techniques you can apply right away.
References
- https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-reasoning
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Program_of_Thought_Prompting

