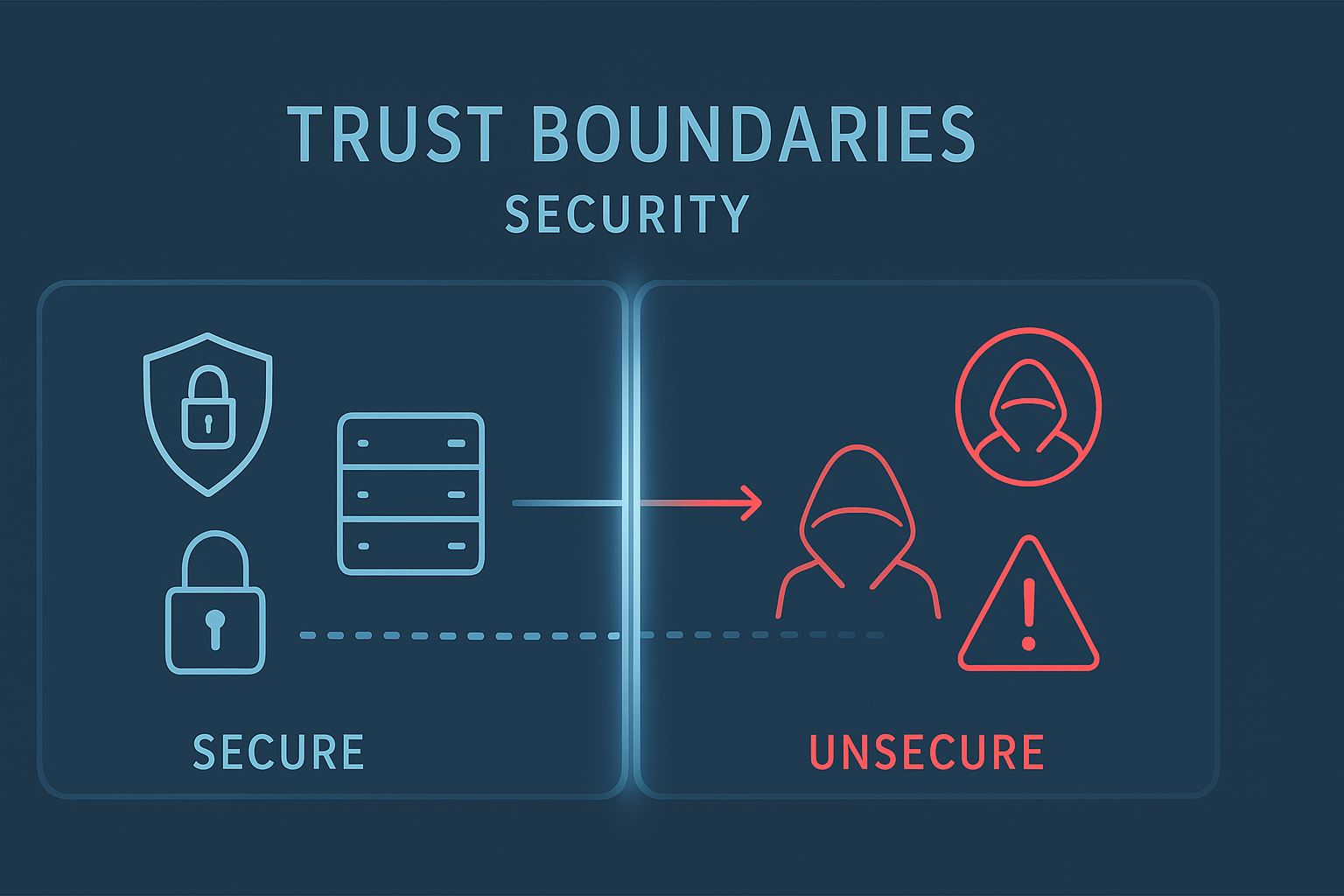
Trust boundaries define critical points in software systems where data crosses between secure and less-trusted zones. Our secure development team sees these invisible barriers every day, from web forms processing user inputs to internal APIs exchanging sensitive information. We’ve learned that identifying these security checkpoints helps determine exactly where to implement controls, much like checking IDs at specific building entry points.
Security teams must understand how data flows across these boundaries to properly safeguard applications. When building defensive layers, developers need clear visibility into these transitions. Read on to discover proven methods for mapping and securing your application’s trust boundaries.
Key Takeaway
- Define where trust changes between system components or networks.
- Limit attack surfaces by separating trusted and untrusted zones.
- Guide the application of access control and security measures.
The Security Challenge: Why Trust Boundaries Matter
Breaches happen all the time. We’ve seen organizations lose millions because they failed to control who or what could cross their security lines. Many breaches result from poorly defined trust boundaries. When unauthorized users access sensitive data or systems, the fallout can be catastrophic, not just financially, but reputationally too.
Preventing such unauthorized access means understanding exactly where those boundaries lie. That’s where trust boundaries become essential, a concept closely tied to how we define trust boundaries in the first place.
They help us control data flow and enforce security rules, ensuring only the right entities get through. Plus, maintaining data integrity and compliance with regulations depends on these boundaries being clear and enforced. Without them, you leave yourself open to risks that can be avoided.
Understanding Trust Boundaries
Trust boundaries are the points inside systems where the level of trust changes. Think of them as borders that separate trusted components, like your internal network or authenticated users, from untrusted ones, such as external networks or anonymous inputs. This isn’t just a theoretical concept. A trust boundary can be thought of as line drawn through a program.
On one side of the line, data is untrusted. On the other side of the line, data is assumed to be trustworthy. (1) We see it in practice whenever a firewall stands between your internal servers and the outside internet or when an application checks whether a user has permission before allowing access to sensitive data.
Key characteristics of trust boundaries include distinct separation lines that clearly mark differences in security privileges and trustworthiness. Crossing these lines means moving from a secure zone into a less secure or untrusted zone. Sometimes, that’s a simple network boundary. Other times, it’s a change in privilege level inside an application where a user might gain admin rights.
Here are some real-world examples we often encounter:
- Firewalls protect internal networks by blocking untrusted external traffic.
- User input from web forms is treated cautiously; it’s sanitized and validated before processing, helping reduce the risk of trust boundary violations that often originate from mishandled external data.
- Applications enforce privilege escalation checks to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive functions.
Why Are Trust Boundaries Essential?
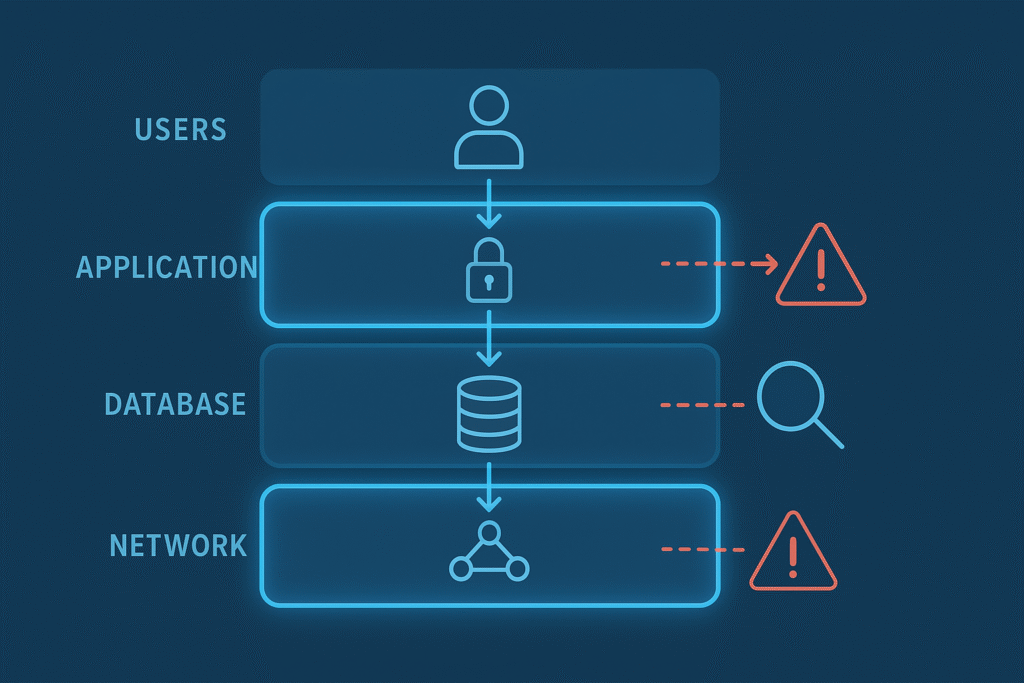
Managing risk is the heart of what trust boundaries do. By defining exactly where trust ends, they help us recognize where threats might come from. This clarity means better control over who or what can access critical assets. When we know these boundaries, it’s easier to design access control systems that only grant permissions to those who need them.
Threat modelling grows more effective when you identify where trust boundaries are crossed, these crossings often represent attack vectors and help you plan targeted defenses. This reflects the broader importance of trust boundaries in threat modeling when structuring system defenses.
Trust boundaries reduce the chances that an attacker who breaches one part of a system can move laterally to more sensitive areas. That containment helps limit damage and supports compliance with data protection laws.
Best Practices for Securing Trust Boundaries
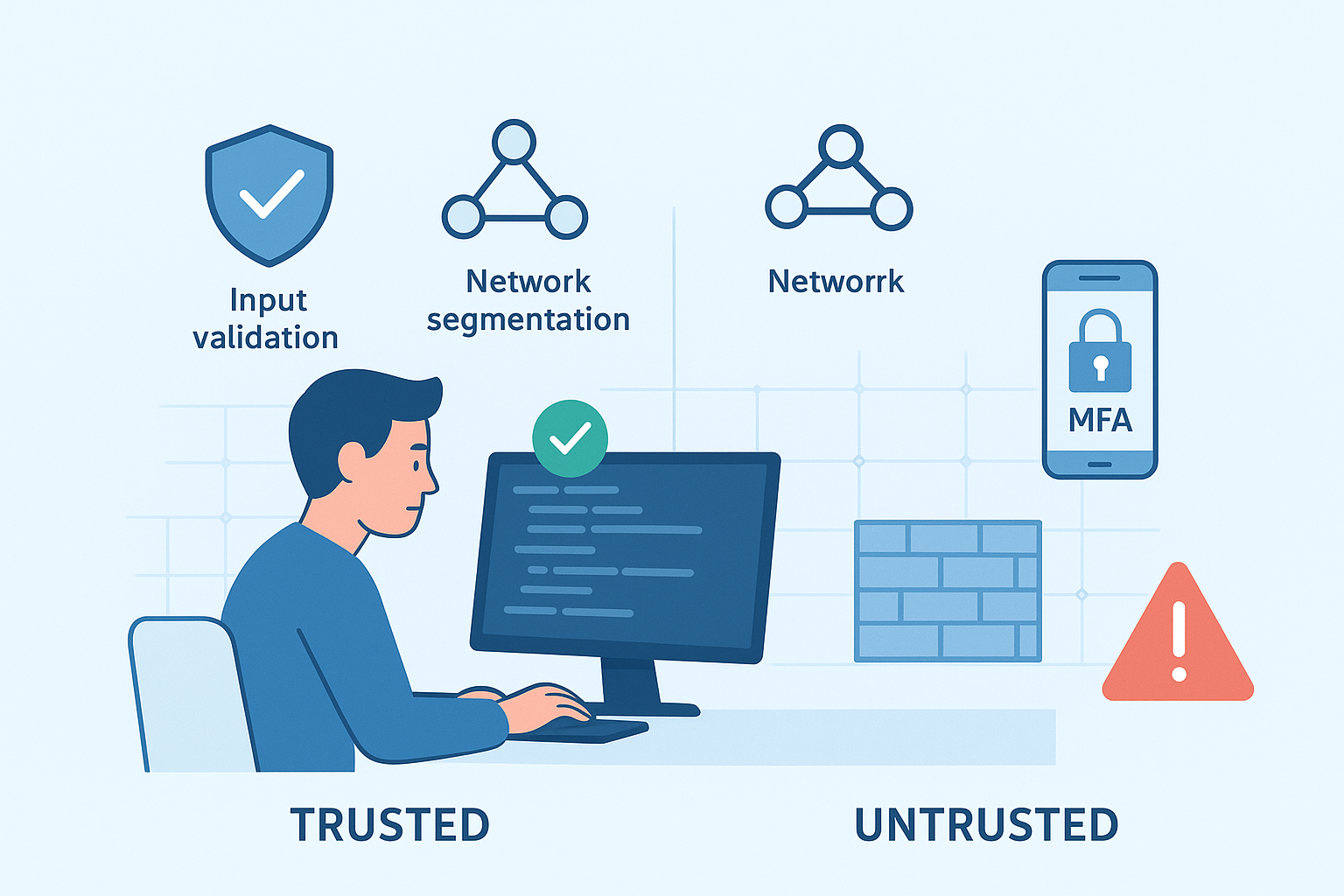
We’ve learned from experience that secure coding practices form the foundation of trust boundary enforcement. Writing code with security in mind helps ensure that boundary crossings happen safely. For instance, validating all input before it touches trusted components reduces risks dramatically.
Network segmentation and firewalls come next. Dividing networks into smaller segments restricts access and limits the spread of breaches. A trust boundary is a dividing line between two areas of a system that have different levels of trust or security. (2) Access control mechanisms, like the principle of least privilege and multi-factor authentication, add layers of defense by ensuring users only have necessary permissions and verifying identities more rigorously.
Data encryption protects sensitive information crossing boundaries, making interception useless to attackers. And don’t forget regular security audits. They reveal any weak points or outdated policies so these can be fixed before trouble strikes.
Here’s a quick list of key boundary security measures:
- Adopt secure coding practices such as validating and sanitising all data crossing a trust boundary.
- Network segmentation paired with firewalls.
- Role-based access control and multi-factor authentication.
- Encryption of data in transit and at rest.
- Scheduled security audits and monitoring.
💡 Pro Tip: Regularly revisit your trust boundaries. Systems evolve, and so do threats. Keeping your definitions up to date keeps you ahead.
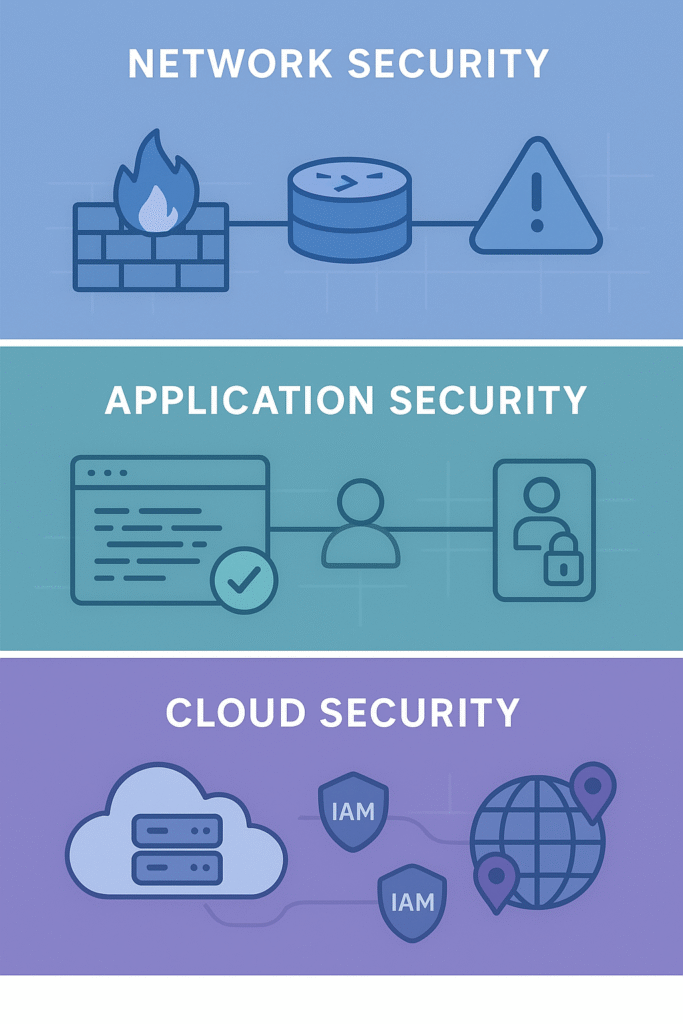
Trust Boundaries in Different Environments
Trust boundaries show up everywhere, but how they’re handled depends on the environment.
In network security, you often see segmentation and isolation in action. We use intrusion detection and prevention systems to watch boundary crossings closely. That way, suspicious activity gets flagged before it’s too late.
Application security relies heavily on input validation and secure coding practices. We’ve personally seen how even small lapses here let attackers exploit vulnerabilities. The boundaries between user roles and privilege levels must be guarded carefully.
In cloud environments, trust boundaries often include identity and access management controls, data-residency borders and third-party service interfaces, each must be clearly defined and enforced. Data residency and compliance rules impose boundaries about where data can live and how it’s accessed. These factors require thoughtful boundary identification and enforcement.
Securing Trust Boundaries: A Practical Outlook
Credits: Gus Nonie
From our experience, the best defense starts with understanding exactly where trust boundaries exist in your system. Not always obvious, these lines can be inside applications, between networks, or at interfaces with third parties.
We recommend embedding secure coding practices into your development cycle. This helps prevent trust violations before they happen. Next, apply network segmentation and strong access controls. Use encryption and authentication protocols to reinforce boundaries.
Monitoring boundaries continuously is crucial. Intrusion detection systems and security audits shine a light on unexpected boundary crossings or potential breaches. They give your team a chance to respond fast.
Remember, trust isn’t a given, it’s earned and must be managed carefully. By defining and protecting trust boundaries, you shrink your attack surface and improve your overall security posture.
FAQ
How do trust boundaries differ from security boundaries in real systems?
Trust boundaries mark where a system’s trust level changes, like between a trusted component and an untrusted component. Security boundaries, on the other hand, define the outer layer of protection, often reinforced by firewalls, security policies, and ingress or egress control. Together, they guide access control and reduce the overall attack surface across networks.
Why is network segmentation important for reducing attack vectors?
Network segmentation and micro-segmentation divide internal and external networks into smaller security zones. This limits lateral movement, isolates vulnerabilities, and prevents privilege escalation. When combined with zero trust principles, access rights and role-based access control ensure that each trust zone and secure zone stays protected, even if one segment is breached.
What role do authentication and authorization play in boundary enforcement?
Authentication verifies who a user is, while authorization confirms what they can do. These controls guard against trust violations when crossing from an untrusted zone to a secure zone. Strong authentication, multi-factor authentication, and secure protocols like TLS ensure secure communication and help maintain data integrity and confidentiality within security domains.
How does cloud security handle boundary crossing and data flow?
In cloud infrastructure, data flow often crosses trust boundaries through third-party interfaces and APIs. Zero trust frameworks and identity management systems use secure gateways, network isolation, and segmentation policies to protect secure data flow. These tools maintain regulatory compliance, prevent data leakage, and safeguard against insider threats and external attacks.
What’s the best way to detect and prevent trust violations or breaches?
Effective breach prevention relies on monitoring boundaries and performing regular security audits. Intrusion detection tools, secure architecture design, and boundary identification help spot vulnerability points and attack vectors early. Strong encryption, data classification, and data protection controls strengthen the system trust level, reduce the threat surface, and improve the organization’s overall security posture.
Conclusion
Trust boundaries security isn’t just a tech term. It’s a vital part of any defense strategy that keeps data safe and systems reliable. By recognizing where trust shifts and applying the right controls, we can reduce vulnerabilities and block attackers from moving freely.
If you want to guard your assets better, start by mapping out your trust boundaries. From there, apply secure coding practices, segment your networks, enforce strict access controls, and monitor continuously. These steps will help you keep threats at bay and protect what matters most.
To strengthen these skills in practice, check out the Secure Coding Practices Bootcamp, a hands-on, expert-led training that helps developers build secure software using real-world coding scenarios. Learn to apply principles like input validation, secure authentication, encryption, and safe dependency use to reinforce your system’s trust boundaries from the ground up.
References
- https://cwe.mitre.org/data/definitions/501.html
- https://moxso.com/blog/what-is-a-trust-boundary

