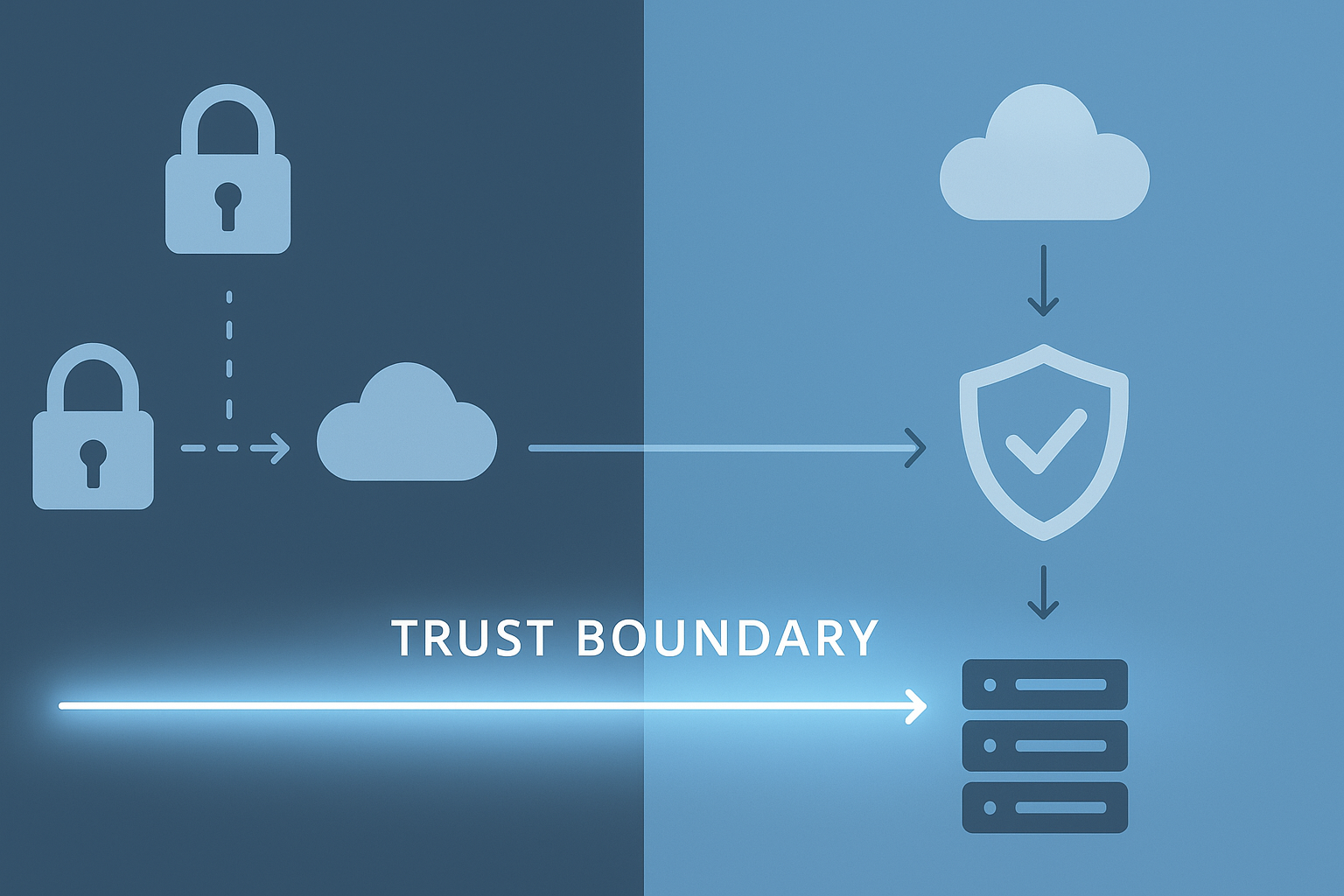
Trust boundaries mark the line where secure meets unsecure areas within software systems. These crossing points need special attention since they’re prime targets for attacks. While working with over 2,000 developers at our bootcamp, we’ve seen firsthand how proper boundary management prevents most data leaks and unwanted access attempts.
Our experience shows that secure coding must be baked into development from day one, not tacked on later. Integrating secure design principles ensures trust boundaries are considered from the start, helping teams catch issues long before deployment. Want to protect your systems better? Read on to discover field-tested methods we use to lock down trust boundaries across applications.
Key Takeaways
- Trust boundaries mark where data or execution changes trust levels, needing strict validation.
- Secure coding practices and network segmentation are essential for protecting these boundaries.
- Regular monitoring and access control reduce risks of trust boundary violations and attacks.
The High Cost of Neglecting Trust Boundaries
Trust boundaries aren’t just a technical detail, they’re often the frontline between safety and disaster. Ignoring them can lead to massive breaches and cyberattacks. We’ve seen firsthand how a small oversight in a trust boundary can allow attackers to move laterally inside a system.
While precise figures vary, misconfigurations and failures around boundary controls (such as segmentation, access control and uncontrolled data flows) are widely cited as major contributors to breaches. The global average cost of a data breach was USD $4.44 million in 2025. (1) That’s a staggering number. It makes the stakes clear: without strong management, sensitive data and systems remain vulnerable.
- Unauthorized access often starts at poorly guarded trust boundaries.
- Data leaks commonly happen when trust boundaries are crossed without validation.
- Attackers exploit these weak points to escalate privileges or move through networks unnoticed.
This is why securing trust boundaries is not optional but essential. Whether it’s your network, application, or cloud infrastructure, defining where trust changes is the first step toward better protection.
Identifying Trust Boundaries: A Step-by-Step Approach
In our work, we start by pinpointing exactly where trust shifts. That means looking at places like:
- Between internal and external networks (think corporate network versus the internet).
- Between user privilege levels – an admin and a regular user don’t have the same trust.
- Between systems or third-party services, where data moves outside your direct control.
- Between cloud services and on-premises infrastructure.
- At any interface where users or data cross from one security zone to another.
We find Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) invaluable here. They let us visualize the flow of data and mark trust boundaries clearly, using dotted lines or boxes. This visual clarity helps us and our team understand where risks lie and plan controls accordingly, a key part of effective threat modeling that strengthens early-stage security analysis. A trust boundary is the point where program data or execution changes its level of ‘trust’. (2)
💡 Pro Tip: Clearly document your trust boundaries using DFDs for better visibility and threat modeling.
When you’re handling complex systems, this clarity is crucial. It’s like having a map that shows where the borders are, so you know exactly where to be cautious.
Securing Trust Boundary Crossings: Micro-Workflows
Credits: TED
Once you identify the boundaries, securing the crossings becomes the main task. We rely on a few key steps:
- Implement strong access controls: Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) ensure only authorized users cross.
- Network segmentation: Dividing networks into smaller zones with different trust levels limits attackers’ movement if they get in.
- Encrypt data in transit using HTTPS or SSL/TLS to protect it from interception.
- Validate and sanitize incoming data to prevent injection attacks or data corruption.
- Monitor and audit all boundary traffic using intrusion detection systems and logs.
💡 Pro Tip: Enforce the principle of least privilege when granting access across trust boundaries.
These aren’t just best practices but necessities. We’ve learned that even small gaps in validation or access control can lead to big problems.
Trust Boundary Violations: Real-World Examples
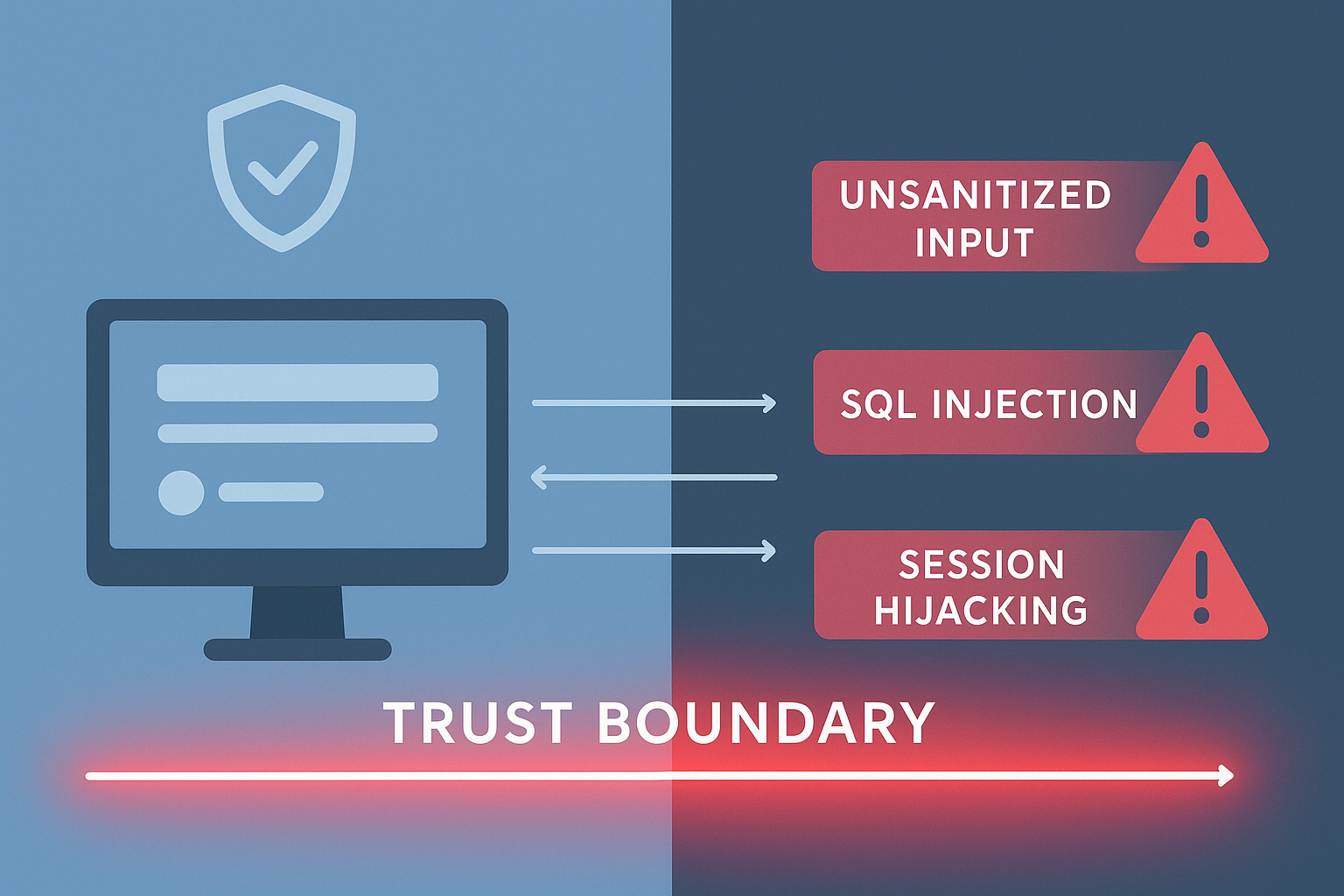
Trust boundary violations are more common than you might think. For example:
- Accepting user input without sanitization, which can lead to SQL injection attacks.
- Using unsanitized data in session states, opening doors for session hijacking.
It’s like leaving your front door unlocked and hoping no one walks in. We’ve seen teams struggle with these simple mistakes, and the fallout can be huge. Regular code audits and secure coding practices help catch these issues early.
💡 Pro Tip: Regularly audit your code for potential trust boundary violations.
Input validation libraries are our go-to tools here. They keep data clean, reducing the risk that untrusted input causes harm.
Network Segmentation: Creating Zones of Trust
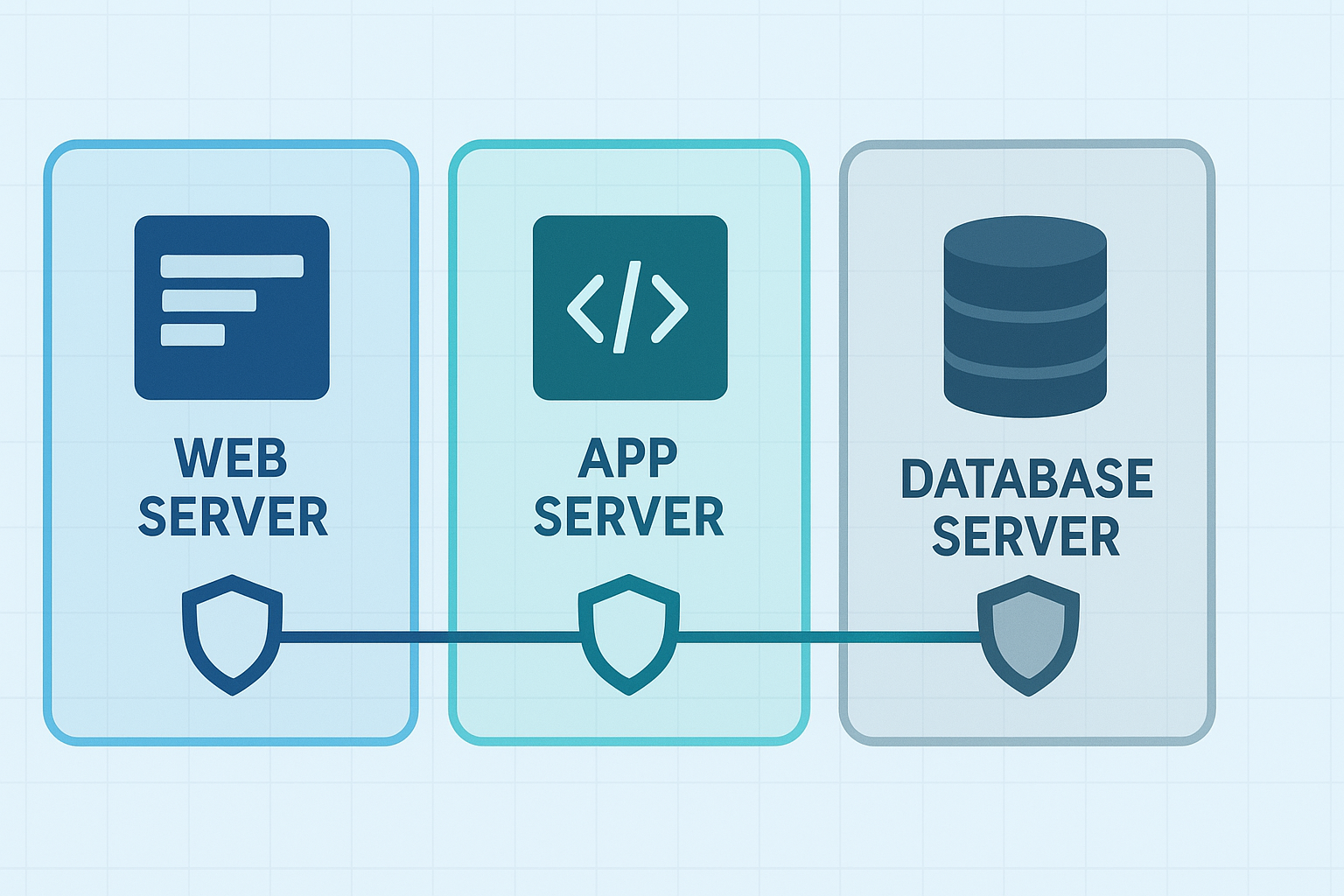
One practical way to enforce trust boundaries is network segmentation. Splitting your network into zones means you can control trust levels more precisely.
- Wireless access points separated from wired internal networks.
- Web servers, application servers, and database servers split into different segments.
This approach reduces unauthorized access risk and limits attack spread if one zone is compromised. From our experience, micro-segmentation, breaking zones down even further, helps secure critical assets better.
💡 Pro Tip: Implement micro-segmentation to further isolate critical assets within your network.
VLANs are a common tool for this, letting you segment and control traffic efficiently, reinforcing the importance of foundational principles in structured network control.
API Trust Boundary Management: A Critical Security Layer
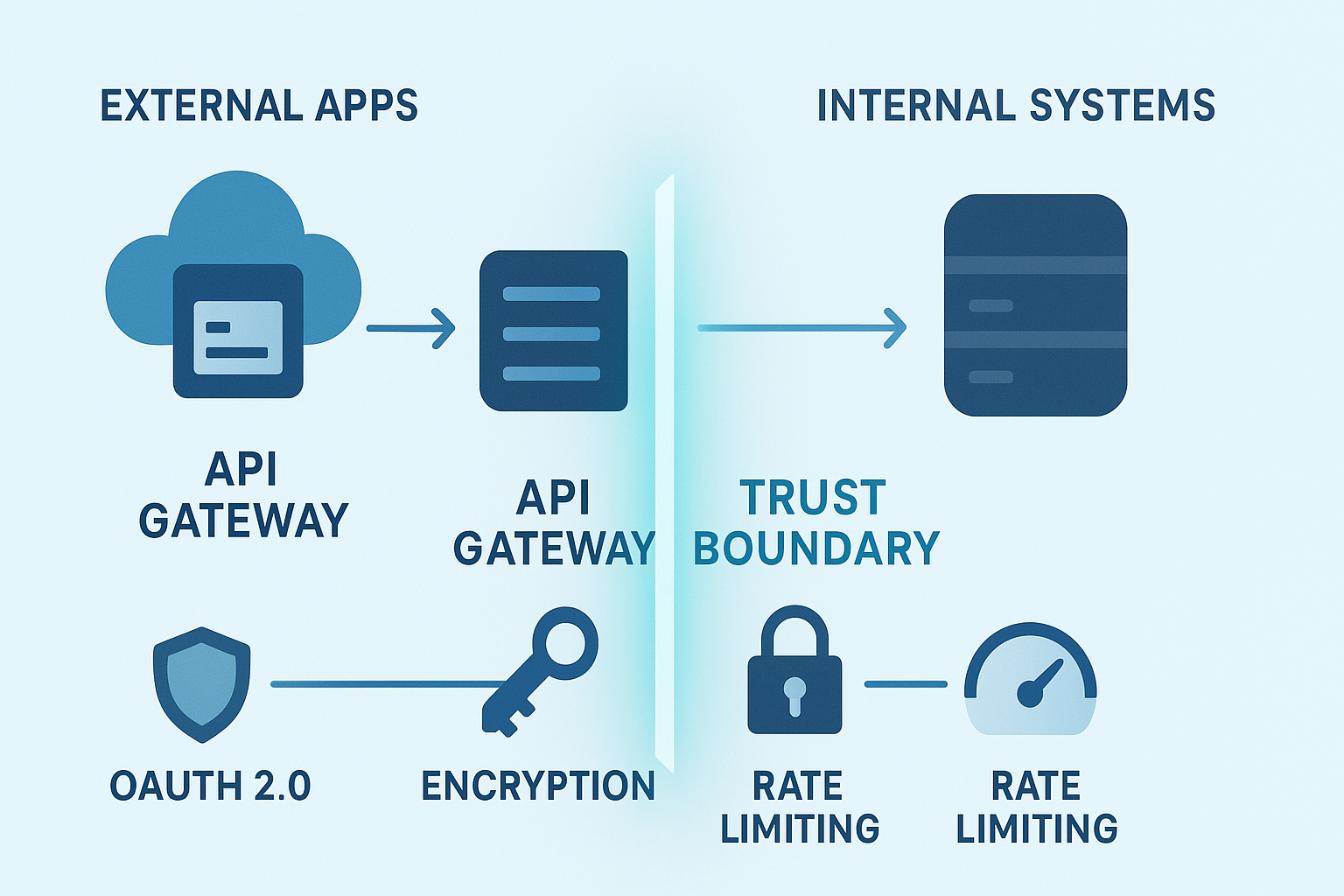
APIs often act as trust boundaries between external or less trusted systems and your internal services. Managing these requires:
- Rigorous authentication and authorization, like OAuth 2.0.
- Input validation to prevent malicious data from causing damage.
- Rate limiting to stop abuse.
- Encryption to protect data in transit.
If you don’t manage these boundaries well, you risk exposing sensitive systems to attackers. We make sure to use API gateways to enforce security policies and monitor traffic at these boundaries, especially when managing trust boundaries across distributed systems.
💡 Pro Tip: Use API gateways to enforce security policies and manage traffic at API trust boundaries.
OAuth 2.0 has been reliable in our experience for securing APIs without causing friction for users. It provides a protective layer that supports clearer trust boundaries when data flows between applications, helping reduce unnecessary exposure of internal services.
Validating Data: The First Line of Defense
At every trust boundary, data should be treated as untrusted until proven otherwise. We always:
- Perform input validation to check data types and ranges.
- Sanitize inputs to remove malicious content.
- Enforce business rules to ensure data makes sense.
- Use type checking to avoid unexpected behavior.
Failing to validate data crossing these boundaries invites attacks like injection or data corruption.
💡 Pro Tip: Implement a data validation framework to ensure consistent and reliable data validation across your applications.
Using a data validation library makes this process easier and more consistent across teams.
Managing Trust Relationships: Establishing Clear Rules
Managing who or what you trust across boundaries is just as crucial. This involves:
- Using encryption keys and certificates to secure communication.
- Employing secure tokens such as JWTs for authentication.
- Regularly reviewing and adjusting access rights follows the principle of separation of duties, ensuring that no single role has unchecked control.
- Granting minimal trust necessary for operation.
- Revoking trust immediately when compromise is suspected.
We’ve seen how lax trust management leads to privilege escalation and breaches. Tight rules and automation reduce this risk.
💡 Pro Tip: Implement a robust key management system to protect your encryption keys.
JWT has helped us securely transmit information between services without exposing credentials.
Checklist for Defining and Managing Trust Boundaries
Here’s a simple framework to keep your trust boundaries solid:
- Identify all potential trust boundaries in your system.
- Assess risks associated with each boundary.
- Implement security controls to mitigate those risks.
- Regularly monitor and audit trust boundary activity.
- Review and update your strategy as systems evolve.
Following this checklist has helped us maintain a stronger security posture over time.
FAQ
What is a trust boundary in cybersecurity, and why does it matter for security?
A trust boundary definition helps show where secure and unsecure areas meet inside a system. In cybersecurity, these points decide who or what can be trusted. Good trust boundaries security reduces the attack surface and protects data flow between internal trust zones, cloud environments, and external interfaces.
How can I identify trust boundaries in software and network systems?
Trust boundary identification starts with mapping how data moves in and out of your system. Use tools like Data Flow Diagrams to mark trust boundary crossings, especially in software architecture, APIs, and cloud security zones. This makes it easier to plan network segmentation, secure communication, and access control policies.
What are some real-world trust boundary violation examples to learn from?
Trust boundary violation examples often involve input validation failures, SQL injection, or cross-site scripting. When a trust boundary data flow crosses without validation, attackers can exploit vulnerabilities. Clear trust boundary firewall rules, session management, and token validation stop these problems before they become data breaches.
How does trust boundary management strengthen zero trust security and compliance?
Trust boundary management systems support zero trust by limiting who can access what across trust zones. Combining micro-segmentation, encryption crossing, and secure protocols helps ensure compliance and system integrity. This approach also protects against privilege escalation, data leakage, and other trust boundary vulnerability risks.
What are the best practices for securing trust boundary authentication and authorization?
Strong authentication and authorization prevent unauthorized trust boundary crossings. Use API gateways, certificate management, and secure coding to guard against attacks. Include audit logs, identity management, and risk assessment in your trust boundary security framework to detect intrusions early and maintain reliable data protection and governance.
Conclusion
You can’t afford to overlook trust boundaries. Defining and managing them carefully protects your data and systems from unauthorized access and attacks. Through secure coding practices, network segmentation, robust validation, and clear trust management, you build a resilient defense. Don’t wait for a breach to start thinking about these boundaries.
Strengthen your security today, join the Secure Coding Practices Bootcamp to learn hands-on methods for building safer software from the ground up. This expert-led, practical training helps developers master real-world techniques like input validation, encryption, and secure authentication, skills that make secure coding part of your everyday practice.
References
- https://www.brightdefense.com/resources/data-breach-statistics/
- https://shostack.org/blog/trust-and-security-boundaries/

