
Privacy starts at the ground floor, not the penthouse. Our dev bootcamp students learn this on day one, when they begin coding their first projects. We’ve seen firsthand how baking privacy into systems from scratch prevents massive cleanup jobs later. This goes beyond dodging fines or patching leaks.
Every piece of personal data deserves care, from the moment it enters our systems until it’s wiped clean. Secure code isn’t a fancy add-on. It’s the foundation that holds everything together. Read on to discover practical ways developers weave data protection into their system blueprints.
Key Takeaways
- Secure coding practices establish a strong foundation for privacy by design.
- Data minimization and transparency are essential to limit risks and empower users.
- Proactive security measures prevent breaches and ensure regulatory compliance.
The Cost of Neglecting Privacy
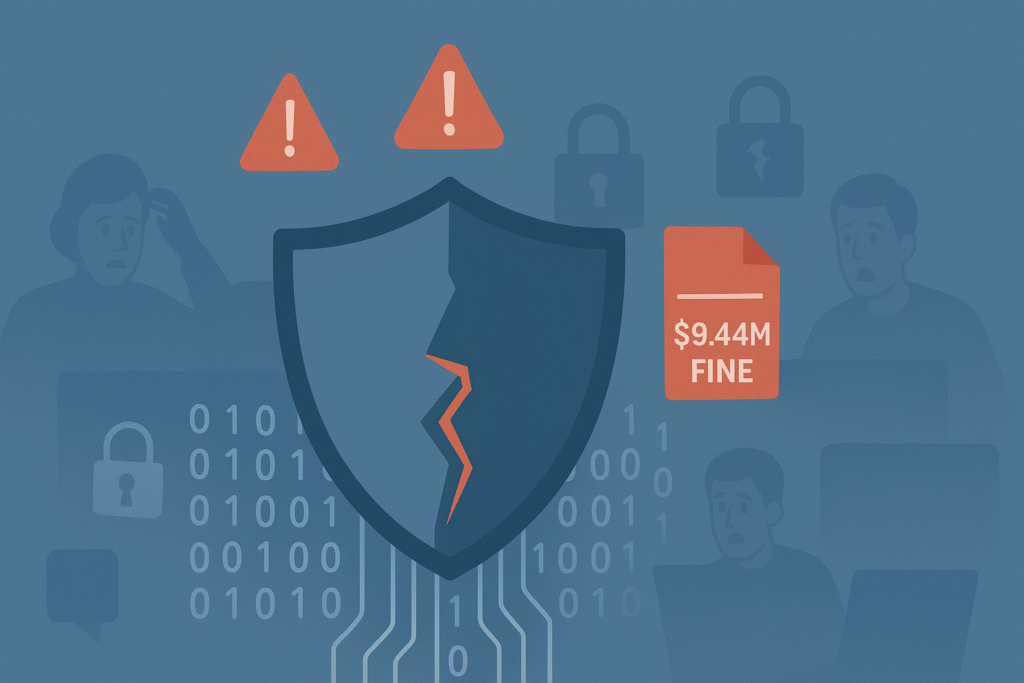
When organizations overlook privacy during system design, consequences ripple far beyond technical glitches. Data breaches expose sensitive information, shaking customer confidence and inviting costly regulatory fines. I remember working on a project where a rushed deployment skipped privacy checks. The fallout was immediate: a six-figure fine and a PR nightmare. According to the 2022 report by Ponemon Institute, the average cost in the US was US$ 9.44 million. (1)
Ignoring privacy is a gamble few can afford. Loss of trust often means losing customers, which hits revenue harder than anyone imagines. But it’s not just about money. Mishandling personal data betrays user trust and undermines fundamental privacy principles.
Here’s why privacy must be a priority from day one:
- Data breaches can cripple businesses financially and reputationally.
- Regulatory compliance demands proactive privacy safeguards.
- User trust hinges on transparent and respectful data handling.
These risks underscore why privacy by design isn’t optional. It’s essential.
Implementing Privacy by Design: Micro-Workflows
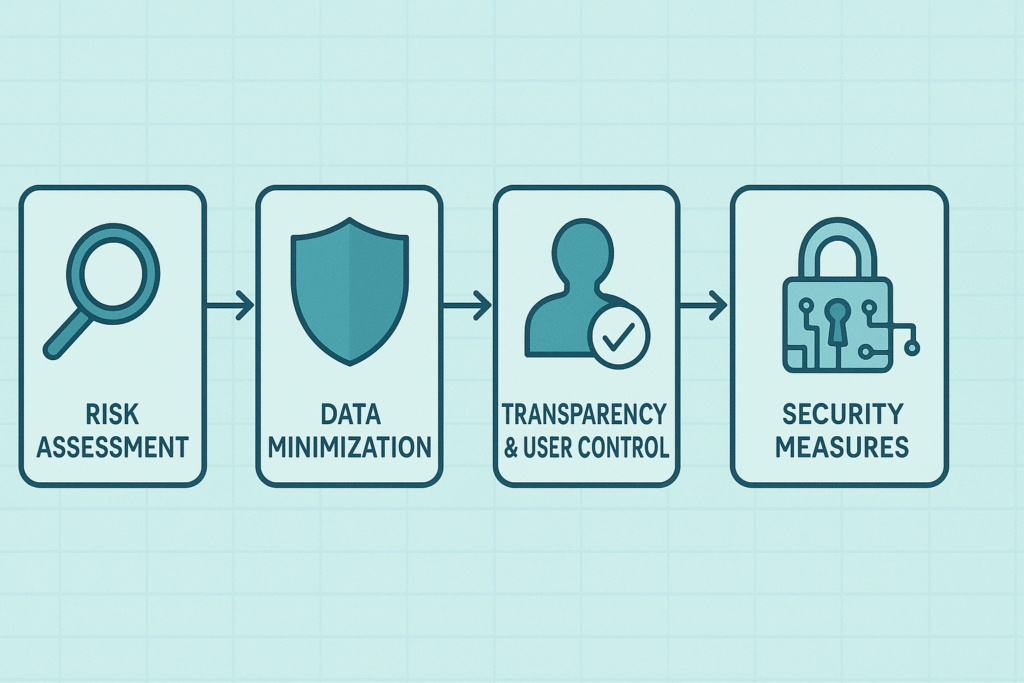
Risk Assessment
The first step in our approach is identifying privacy risks early. We don’t wait for problems to surface. Instead, we integrate risk assessment into the secure-by-design methodology that ensures security and privacy are part of every phase before writing a single line of code. These assessments help us spot potential privacy pitfalls tied to new features or data flows.
For example, a PIA checklist for new software development might include:
- What personal data is collected and why?
- How will data be stored and secured?
- Who has access and under what controls?
- Are there potential risks if data is exposed?
- What mitigation strategies can prevent those risks?
Taking this step early prevents costly redesigns and ensures privacy is baked in, not bolted on.
Data Minimization
We’ve learned that collecting less data is often more powerful than collecting a lot. Data minimization is defined as collecting only the personal information necessary for the task. (2) The fewer personal details stored, the smaller the attack surface. So, we focus on gathering only what’s absolutely necessary for the task. During user registration, for instance, we ask only for essential information, no extra details that don’t serve a clear purpose.
Limiting data access is just as critical. Not everyone on the team needs full access to user data. Role-based access controls ensure only authorized personnel see sensitive info. Anonymization techniques then further protect data by stripping identifiers where possible.
Here’s what data minimization looks like in practice:
- Collect essential user data only during sign-up.
- Restrict data access based on roles and responsibilities.
- Apply anonymization or pseudonymization to reduce exposure.
These steps shrink privacy risks and help comply with privacy regulations like GDPR.
Transparency and User Control
Users deserve to know exactly how their data is handled. We make privacy notices clear, straightforward, and easy to find. Consent management comes next, no sneaky opt-ins or confusing jargon. Just clear options so users feel in control. These practices echo the secure design principles overview, which stress transparency and user empowerment as cornerstones of secure systems.
Respecting data subject rights means enabling users to access, correct, or delete their data when requested. It’s part of embracing a privacy-first mindset that values user autonomy.
One effective tool is a user-friendly consent form where:
- Users can easily grant or withdraw permission.
- Data practices are explained in plain language.
- Choices are respected without unnecessary friction.
This transparency builds trust, making users confident their data is safe and respected.
Security Measures
Credit: Mike Chapple
Even with the best intentions, privacy fails without solid security. Encryption techniques guard data both in transit and at rest. We implement multi-factor authentication to tighten access control. Our secure coding practices reduce vulnerabilities from the start, making it harder for attackers to exploit flaws. These controls reflect the core principles of secure system design that emphasize layered defenses and fail-safe defaults.
For example, encrypting sensitive fields and deploying role-based access controls are standard. We also embed security protocols into system architecture, ensuring all components follow strict security guidelines.
Some key security controls include:
- End-to-end encryption methods to protect data flow.
- Secure software development lifecycle integrating security at every phase.
- Incident response plans ready to tackle potential breaches swiftly.
Security by design complements privacy by design, forming a comprehensive defense against threats.
Privacy by Design in Action: Our Experience
Over time, we’ve seen how privacy engineering transforms projects. One healthcare app we helped develop started with a secure coding foundation. We layered in data minimization, clear privacy notices, and robust encryption. The result? A product users trusted with their most sensitive info, and the team avoided any regulatory stumbles.
The process wasn’t flawless, but continuous privacy audits and privacy risk management kept us on track. We treated privacy as a living framework, adapting as features evolved and threats emerged. This hands-on approach led to a smoother rollout and much less firefighting later.
Practical Advice for Adopting Security Privacy by Design
If you’re aiming to make privacy a core feature rather than a checkbox, start with secure coding practices. Train developers to write code that anticipates security flaws and data leaks. Pair that with early privacy impact assessments to catch risks before they grow.
Focus on data minimization, not just because regulations require it, but because it reduces your exposure. Be transparent with users and give them real choices about their data. And don’t forget to build strong security controls into your system architecture, from encryption to access restrictions.
Remember, privacy by design is a mindset, not just a process. It requires ongoing attention and collaboration across teams. But the payoff is worth it: stronger data protection, happier users, and fewer headaches down the line.
FAQ
How does privacy by design protect personal data security from the start?
Privacy by design means thinking about personal data security early in system design security. Developers apply secure coding practices, access control, and encryption techniques to keep information safe. These privacy by design principles help prevent data breaches, protect data integrity, and ensure every step of the data lifecycle supports privacy safeguards and data protection.
What’s the difference between privacy engineering and privacy compliance?
Privacy engineering focuses on building technical privacy controls, like privacy-enhancing technologies, data anonymization, and pseudonymization, directly into products. Privacy compliance ensures these systems meet regulatory compliance standards such as GDPR compliance and other privacy regulations. Together, they bridge technology and law, guiding teams to create secure software development processes that respect user data protection and privacy standards.
Why is data minimization so important for privacy and security?
Data minimization limits how much personal information an organization collects and keeps. Fewer details mean fewer risks if data is exposed. This principle supports data breach prevention, privacy transparency, and secure data storage. It’s one of the simplest privacy best practices that reinforces overall information security, regulatory compliance, and confidential data handling within privacy governance frameworks.
How can organizations handle user consent management and privacy transparency better?
Organizations should make privacy policies easy to read and user-friendly. Clear user consent management lets people decide how their personal data is used. Combining privacy controls, secure communication, and privacy-enhanced user experience builds trust. Regular privacy audits, privacy training, and privacy monitoring also help ensure ongoing transparency and stronger privacy assurance for both users and companies.
What tools help maintain strong privacy and security architecture?
Teams use privacy risk management frameworks, threat modeling, and secure design patterns to strengthen security architecture. Privacy impact assessment and privacy risk assessment tools identify weak points early. Alongside cloud privacy safeguards, data encryption methods, and secure development lifecycle practices, these privacy frameworks and privacy maturity metrics keep systems compliant and ready for evolving cybersecurity threats.
Conclusion
Privacy by design is more than a buzzword. It’s a necessity to protect personal data and preserve trust. Secure coding practices provide the groundwork, enabling data minimization, transparency, and security controls to flourish naturally. Secure coding practices (such as input validation, secure authentication) reduce the risk of data exposure. Ignoring privacy invites costly breaches and lost customers, but embedding it from the start changes everything.
For those building systems or products, the call is clear: prioritize privacy as you design and develop. Keep privacy principles at the heart of your workflows. That way, you safeguard not only data but your organization’s reputation and future.
If you want to strengthen your approach, start by reviewing your secure coding standards, ramp up privacy impact assessments, and engage your team in privacy training. Privacy by design is a continuous process, but one well worth the effort.
Ready to turn privacy principles into practice? Strengthen your secure coding and privacy-by-design approach with hands-on training from the Secure Coding Practices Bootcamp. Learn directly from experts, code in real-world scenarios, and build safer software from day one.
References
- https://technologymagazine.com/articles/data-breaches-cost-an-average-9-44m-in-the-us-last-year
- https://www.piiano.com/blog/data-minimization

